Converting 3V to 5V involves using a circuit called a boost converter.
Boost converters take a lower voltage input and increase it to a higher voltage output.
In this case, it would take the 3V from your source like a battery and bump it up to 5V to power your device.
Circuit Working:
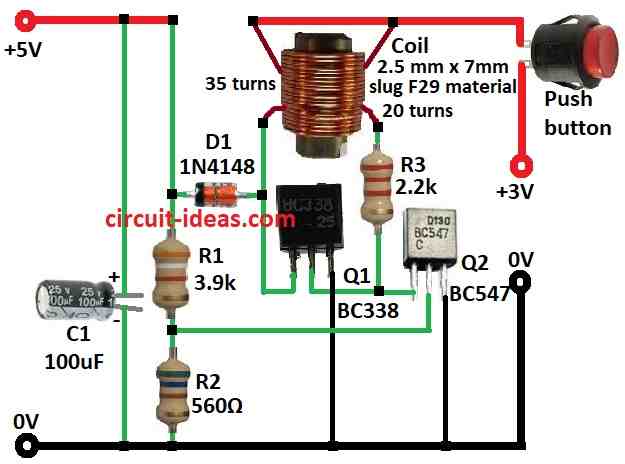
Parts List:
| Category | Component | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 3.9k | 1 | 1/4 watt |
| 560Ω | 1 | 1/4 watt | |
| 2.2k | 1 | 1/4 watt | |
| Capacitors | Electrolytic 100µF 25V | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | Transistor BC338 | 1 | |
| Transistor BC547 | 1 | ||
| Diode | 1N4148 | 1 | |
| Coil | 2.5mm x 7mm slug F29 material | 1 | 35 turns, 20 turns |
| Other Components | Push button | 1 |
In this article we will work on how to convert 3V to 5V boost converter.
In our boost converter circuit takes in a lower voltage input of 3V and generates a boosted output of 5V.
This circuit works by interrupting the current from the battery with transistor Q1 BC338 and storing the energy in the inductor.
When the transistor turns off, the energy stored in the inductor creates a voltage spike that is higher than the battery voltage, which is then rectified by the diode 1N4148 and filtered by the capacitor to provide a regulated 5V output.
The 3.9k and 560 ohm resistors form a voltage divider network that is used to set the reference voltage.
Formulas:
Several crucial calculations and considerations must be made when designing a boost converter circuit in order to assure effective voltage conversion from a lower input voltage 3V to a higher output voltage 5V.
These are the fundamental equations and procedures for creating a circuit for a boost converter:
Calculate Duty Cycle D:
The boost converters duty cycle D may be found by dividing the output voltage Vout by the input voltage Vin:
D = Vout / Vin
here in our circuit,
D =5V / 3V = 5 / 3 = 1.67
Determine the Lowest Inductor Value L:
The following formula may be used to get the inductance value:
L ≥ (Vout−Vin) * Vout / f*ΔI
where,
- The minimal input voltage is denoted by Vin 3V.
- The output voltage is denoted by Vout 5V.
- The frequency of switching is f.
- Peak to peak inductor current ripple is represented by ΔI.
ΔI typically ranges from 20% to 40% of the average output current.
Note:
The components listed above will typically be configured in a boost converter circuit design in order to perform the voltage boosting capability while maintaining stability and efficiency.
Keep in mind that the precise values of the components and the particulars of the design could change depending on your needs and the capabilities of the components you select.
To get the desired performance, design iterations and simulation are advised.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Boost Converter Circuit from 3V to 5V, steps are mentioned below for connections of components:
- The collector of transistor Q1 is connected to one end of the inductor.
- The other end of the inductor is connected to the anode of diode D1 1N4148.
- The positive terminal of the capacitor C1 100uF is connected to the output of +5V.
- The negative terminal of the capacitor C1 is connected to the ground.
- The base of transistor Q1 is connected to a series of resistor R3 and a coil.
- The emitter of transistor Q2 is connected to the ground.
- The base of transistor Q2 is connected to a voltage divider network consisting of two resistors R1 and R2.
- The collector of Q2 is connected to R3 resistor and a coil.
- The positive side of the voltage divider network is connected to the +5V output.
- The negative side of the voltage divider network is connected to the ground.
- Connect a push button to the positive supply of +3V.
Note:
- Please double check the connection.
- Take extra care while handing the electrical items when in use.
Conclusion:
If you have some experience with electronics, a boost converter IC offers a more customizable approach.
These integrated circuits require a few additional external components like capacitors and inductors but they are still simpler to build than a circuit from scratch.
Leave a Reply