Main purpose of Simple DC Over Voltage Protector Circuit is to save electronic parts or circuits from damage when voltage from DC power source become too high.
In many uses, case where stable and fixed voltage is needed this type of circuit are very useful.
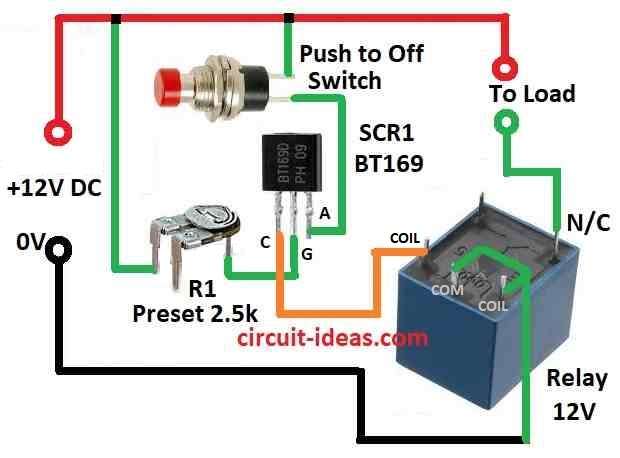
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
A normally closed 12V relay is connected with one SCR.
This SCR is put on 12V supply line.
SCR gate part is used to check the voltage level.
When voltage is under limit SCR1 does not work but relay stay closed so current goes to load.
But when voltage goes above 12V SCR1 gate get enough current.
Then SCR1 turns ON, relay also turn ON and break the current to load.
This stop extra voltage go to load and protect it from damage.
R1 is used to set when SCR1 should turn ON.
When SCR1 turns ON relay opens and stop current to load.
Formulas:
DC Over Voltage Protection Circuit need some calculation like this:
1. Voltage Divider Calculation:
To turn ON the SCR we use voltage divider to get one reference voltage (Vref).
We use one fixed resistor (Rf) and one preset resistor (Rp) like this:
Vref = Vin × Rp / (Rp + Rf)
- Vref is the voltage we want to turn ON SCR.
- Vin is the input voltage, in our circuit it is 12V.
- Rp is the preset resistor.
- Rf is the fixed resistor both in series
2. Gate Resistor for SCR:
We need to give correct current to SCR gate to turn it ON and for that we need to use resistor Rg.
Gate current (Ig) can be found in SCR datasheet which is normally between 10 to 50 mA.
Ig = (Vgate − Vref) / Rg
So to find Rg:
Rg = (Vgate − Vref) / Ig
- Vgate is the voltage at gate which is normally 1 to 2V.
- Vref is the voltage from divider.
- Ig is the current from datasheet.
- Rg is the resistor we calculate.
3. Relay Coil Current:
Relay coil need enough current to turn ON so we need to heck if SCR can give this current.
Irelay = Vsupply / Rcoil
- Vsupply is the 12V relay power.
- Rcoil is the resistance of relay coil.
- Irelay is the current that go in coil.
4. SCR Power Dissipation:
Check how much power the SCR is using when ON.
PSCR = VT × Iload
- VT is the voltage drop on SCR when ON from datasheet which is usually 1 to 2V.
- Iload is the current through load or relay.
- PSCR is the power SCR is using.
Use these formulas to design good circuit.
But always check with actual parts and datasheet to be sure.
Adjust values based on our component rating.
How to Build:
To build a Simple DC Over Voltage Protector Circuit following steps are required for connections and assembling:
- Connect positive side of 12V power to one side of load.
- Connect other side of load to NC Normally Closed contact of relay.
- Connect common pin of relay back to positive of 12V supply.
- Connect SCR1 anode to the point where load and relay contact are joined.
- Connect SCR1 cathode to negative side of 12V power.
- Connect one preset resistor R1 between SCR1 gate and point where load and relay are joined.
- Also connect SCR1 gate to same point of load and relay.
Notes:
- Change preset to R1 to set trigger voltage when overvoltage protection will work.
- Be sure all parts can handle the voltage and current we are using.
- Check all wiring polarity carefully so nothing gets damaged.
- Use a good box/enclosure to keep the circuit safe.
- If we are not sure please take help from someone who knows electronics.
Conclusion:
This Simple DC Over Voltage Protector Circuit helps to protect devices from high voltage damage.
Choosing the correct components gives good result and keeps voltage under control.
It is a very useful and important safety circuit for systems that need stable voltage.
Leave a Reply