Cascode amplifier is 2-stage circuit which is used in analog electronics.
It gives better gain, bandwidth, input and output impedance.
Mix of common source and common gate amplifier helps reduce miller effect and gives more stability.
It is used in RF amps, fast op-amps and instruments.
This article for Simple Cascode Amplifier Circuit teaches us about FET Cascode amp how it works, formulas, real circuit making and the tips required while making.
Circuit Working:
Working of FET cascode amplifier circuit:
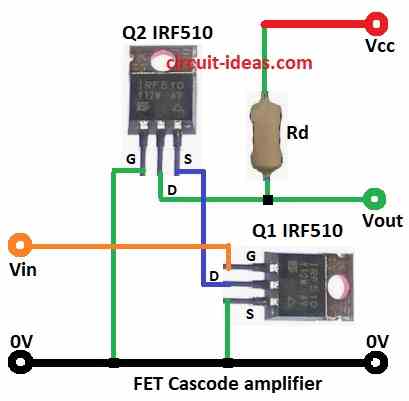
Cascode amp circuit with FET has two parts.
First part is common source FET with input Vin goes to its gate.
Second part is common gate FET which is powered by first stage.
Rd is drain resistor in output stage.
Vout taken from drain of Q2.
Q2 gate is at ground so Q2 source and Q1 drain stay almost at same voltage.
Q2 gives low input resistance to Q1.
This lowers gain of Q1, but also reduces Miller effect for better bandwidth.
Q2 makes up for Q1 gain loss so total gain stays good.
Q2 is not much affected by Miller effect.
Capacitance charge/discharge goes through Rd and load which affects only a very high frequencies.
Formulas:
Here are basic formulas for FET Cascode amplifier:
Voltage Gain (Av):
Av = gm × Rd
where,
- gm is FET transconductance
- Rd is drain resistor of Q2
Input Impedance (Zin):
where,
Zin = Rg1
- Rg1 is gate resistor of Q1
Output Impedance (Zout):
Zout = Rd
where,
- Rd is drain resistor of Q2
Bandwidth (BW):
BW goes up because Miller effect is small with following formula:
BW ∝ 1 / (Cgd × Av)
where,
- Cgd is gate-drain capacitance
Working of realistic cascode amplifier circuit:
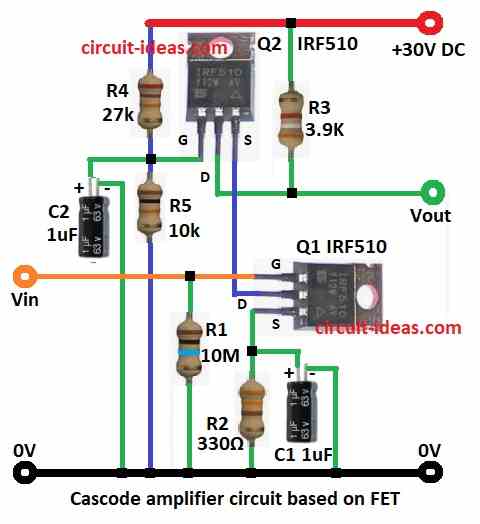
Parts List:
| Component Type | Value | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors (All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified) | 10M | 1 |
| 330Ω | 1 | |
| 3.9k | 1 | |
| 27k | 1 | |
| 10k | 1 | |
| Capacitors | Electrolytic 1µF | 1 |
| Semiconductors | FET IRF510 | 2 |
Real FET cascode amp circuit shown is above.
R4 and R5 make voltage divider and give bias to Q2.
R3 is drain resistor of Q2 and controls drain current.
R2 is source resistor of Q1.
C1 is bypass capacitor for R2 which improves the gain.
R1 keeps gate of Q1 at zero volts when there is no input signal.
Formulas:
Below are the formulas for the realistic FET cascode amplifier:
Voltage Gain (Av):
Av = gm × R3 / (1 + gm × R2)
where,
- gm is the 2ID / (VGS − Vth)
- R3 is the drain resistor of Q2
- R2 is the source resistor of Q1
Input Impedance (Zin):
Zin = R1
where,
- R1 is the gate resistor of Q1
Output Impedance (Zout):
Zout = R3
where,
- R3 is the drain resistor of Q2
Bias Current (ID):
ID = (VGS − Vth) / R2
where,
- VGS is the gate to source voltage
- Vth is the threshold voltage
Coupling/Bypass Capacitors (C1, C2):
Xc = 1 / (2πfC)
where,
- Xc should be low vs R at working frequency
Bandwidth (BW):
BW = 1 / (2π × Rd × Cgd)
where,
- Cgd is the gate-drain capacitance of Q1
- Rd is the drain resistor R3
Note: Miller effect is small with BW is better.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Cascode Amplifier Circuit follow the below mentioned connections steps:
- Q1 gate pin connect to Vin through R1 and also to GND
- Q1 source pin connect to GND through R2
- Q1 source pin also connect C1 from this pin to GND of bypass capacitor
- Q1 drain pin connects to Q2 Source
- Q2 gate pin connects to (+) of C2 and (–) of C2 to GND
- Q2 gate pin also connect R4 to +V and R5 to GND of voltage divider bias
- Q2 drain pin connects to Vout through R3 to +V
- Q2 source pin is already connected to Q1 drain pin
Conclusion:
Simple Cascode Amplifier Circuit is smart circuit.
It gives high gain and works on wide frequencies and has less problem from Miller effect.
It mixes common source + common gate and keeps signal clean which is good for high speed.
With right biasing and capacitors the circuit becomes strong and stable.
It is best for RF, fast op-amps and accurate systems where bandwidth matters.
Leave a Reply