Have anyone tried using a toy which needs 3.3V but charger gives only 5V? That too much power!
This article for How to Convert 5V to 3.3V Circuit is like small helper.
It take strong 5V and make it weak 3.3V which is right for device.
This help when USB or charger give more power than needed.
There are many ways to make this circuit and each way can be good and bad.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Category | Component | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 47Ω 1/4 watt | 1 |
| Semiconductors | Diode 1N4148 | 3 |
| Zener Diode 3.3V | 1 |
This is simple 5V to 3.3V converter circuit using diodes and resistor.
Each diode drops around 0.7V so output is not 3.3V but it goes down to around 2.2V.
This circuit waste power as heat which is not efficient.
It gives only small current to about 10mA.
It is not good if we need more power.
Output voltage changes with input and load.
For better options:
Voltage divider with two resistors are cheap and easy but gives weak current.
Linear regulator are more stable with more current and is better than divider.
Switching regulator are best and most efficient but are more complex.
Formulas and Calculations:
We can use resistor and Zener diode to change 5V to 3.3V.
Here are some simple steps:
1. Find Resistor Value R:
Use formula:
R = (Vin – Vout) / Iz
where:
- Vin is the 5V input
- Vout is the 3.3V output
- Iz is the Zener current example: 30mA or 0.03A
Example:
R = (5V – 3.3V) / 0.03A = 1.7V / 0.03A = 57Ω
Choose standard resistor near this like 47Ω or 68Ω.
Important Notes:
Resistor and Zener must handle the power safely.
Power = Iz² × R
Output voltage may change if load changes.
Check part tolerance for better accuracy.
This method is simple and cheap which is good for small load.
How to Build:
How to Convert 5V to 3.3V Circuit below mentioned are the simple steps for connections:
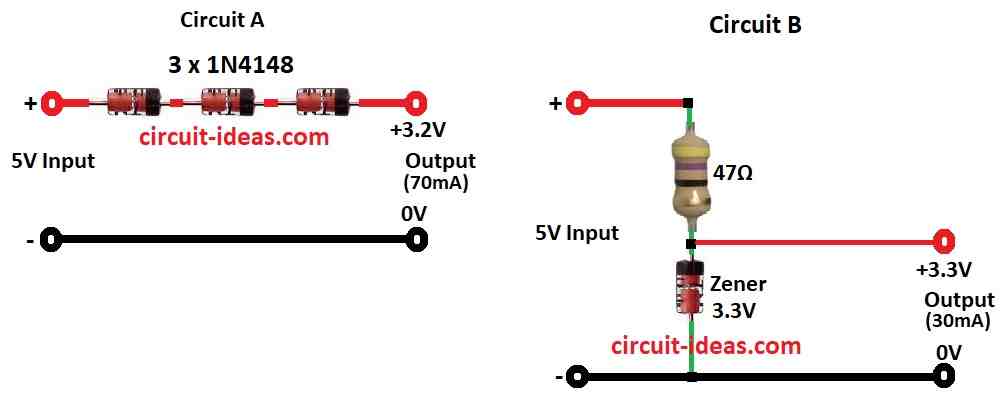
Circuit A:
- Three 1N4148 diodes in series connect to positive side.
- These are small signal diodes used in many simple circuits.
Circuit B:
- One 47 ohm resistor and one Zener diode connect from output to ground (negative side).
- Resistor controls current and Zener keeps voltage at 3.3V.
3.2V 70mA:
- Looks like power source that gives 3.3V and up to 70mA are not part of main circuit.
3.3V 30mA:
- Another 3.3V source gives 30mA which is also not part of main circuit.
47Ω:
- This resistor 47Ω helps to limit current to about 30mA.
Conclusion:
How to Convert 5V to 3.3V Circuit help change 5V to 3.3V so we can use low-voltage device with USB power.
Which circuit to use depends on what our device needs which might be simple or strong and low or high current.
Leave a Reply