Simple BFO circuit is small electronic circuit which make signal sound when mix with other signal.
This circuit help to hear weak radio signal like in old radio or metal detector.
It is easy to build and uses one transistor part called a bipolar junction transistor (BJT).
What is Beat Frequency Oscillator:
BFO are used in getting SSB single sideband)and CW continuous wave signal.
It make one signal that mixes with IF output from detector and make AM signal.
Then detector remove this AM signal.
When mode switches and connects to ‘C’ or SSB then BFO turns ON.
Circuit Working:
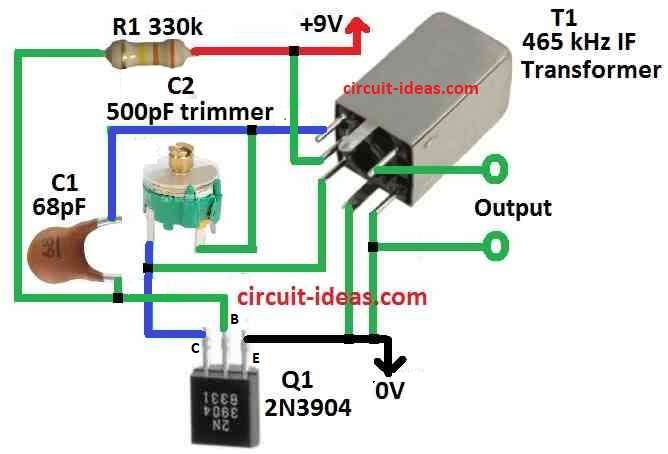
Parts List:
| Category | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 330k 1/4 W CFR | 1 |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 68pF | 1 |
| Trimmer 500pF | 1 | |
| Semiconductor | Transistor 2N3904 | 1 |
| Transformer 465 kHz IF | 1 |
This LC oscillator uses one BJT transistor for make BFO.
This simple circuit and explanation show the following:
Resistor R1 gives right power to BJT Q1 so it works good.
BJT collector connect to main coil of 465 kHz transformer L.
Second coil give feedback to keep oscillation going.
Transformer and variable capacitor C1 set the frequency like in Hartley oscillator.
To change tuning we remove transformers built-in capacitor and use C1 instead.
When C1 value is changed frequency also changes.
BJT collector give output signal and this signal is used for beat frequency and more.
Output frequency goes from 465 kHz to 1.7 MHz by moving C1.
This setup gives easy way to make signal in that range.
We can change parts to fit what we need by testing and adjusting the values.
Formulas:
The frequency f of LC oscillator is found using this formula from Hartley oscillator:
f = 1 / 2π√(L × C)
where:
- f is frequency in hertz Hz.
- 2π means 2 times pi which is about 3.14159 used in many wave and signal formulas.
- L is inductance of coil in henries H where coil stops fast to change in current.
- C is capacitance of capacitor in farads F where capacitor store energy in electric field.
- √ means square root.
This formula say: if L or C become big then frequency f become small.
So more capacitance or more inductance = lower frequency.
Less capacitance or inductance = higher frequency.
How to Build:
Below mentioned are the building steps for Simple Beat Frequency Oscillator (BFO) Circuit:
Bias in Transistor:
- Be sure BJT have correct bias to work stable and to put it in right setup.
- One tuned 465 kHz transformer connect to transistor Q1 collector.
Transformer Setup:
- Use normal Hartley oscillator setup with this transformer.
- Main coil and feedback coil must connect in correct way to start oscillation.
Tuning Control Change:
- Remove transformers own tuning capacitor.
- Then use variable capacitor C1 to change frequency.
Frequency Range Change:
- Move C1 to change output frequency.
- It can go from 465 kHz to 1.7 MHz.
Uses:
- To check frequency put nearby radio that can get normal broadcast signals.
- Make beat sound by setting generator to radios IF intermediate frequency.
- This help hear SSB single sideband or CW continuous wave signals.
Conclusion:
Engineers and hobby people can build this Simple Beat Frequency Oscillator (BFO) Circuit easily.
It has wide frequency range and can work as BFO or local oscillator.
This circuit is good for testing or using in actual circuit.