Want to change how bright the LED light is?
We can use adjustable LED dimmer circuit for that.
This small and Simple Adjustable LED Dimmer Circuit helps to control LED brightness so one get just right light for any time.
By turning some parts like resistor, transistor and one special knob (called potentiometer), this circuit change how much power the LED will requires to make it more bright or more dim as one likes.
Circuit Working:
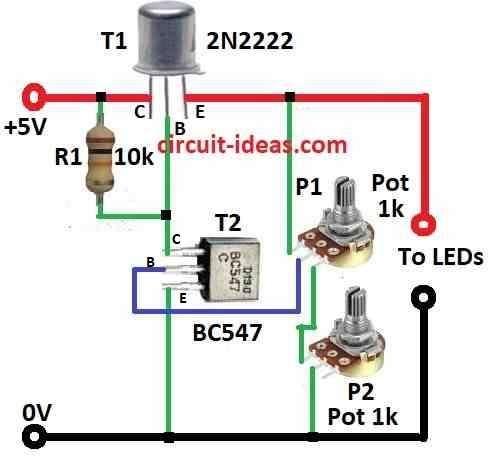
Parts List:
Here is one easy LED dimmer circuit which uses only 2 transistors, 1 resistor and 2 potentiometers.
Normal LED display use around 25mA for each segment so we usually need resistors to stop too much current.
If we use 6 digit display we need around 42 resistors in series, that is too lot!
But this LED dimmer fixes that problem It lets control brightness with only few parts.
No need of many resistors so PCB is easier to make and put together.
This circuit work like voltage regulator and it gives power that one can change.
LED brightness goes up or down when voltage changes this voltage change is done by the regulator.
Potentiometer P1 is for big brightness change and P2 is for small fine adjust.
This circuit can change voltage from 0 to 4.3 volts.
To use it first turn both potentiometers to zero and then slowly turn them until light is good for anyone.
In 6 digit display total current must not go more than 1 ampere.
For example each segment take 25mA. 6 digits × 7 segments = 1050mA (a little more than 1 amp).
Because of this big current transistor T1 can get hot and so it need good heat sink to keep it cool.
Formulas:
Current Going Through LED:
To know how much current will the LED require one needs to know two things:
- LED working current (ILED)
- LED forward voltage (VLED)
The resistors and transistors in circuit also change how much current goes to LED.
Formula:
ILED = (VCC − VLED) / RLED
where:
- VCC is power supply voltage
- VLED is the forward voltage of the LED
- RLED is total resistance in line with LED (can be from resistor, potentiometer or effect of transistor)
In this circuit RLED means the load resistance which is changed by turning the potentiometer and transistor working.
Potentiometer Resistance and Controlling Current:
The small transistor BC547 get base current from potentiometer.
This current then controls big transistor 2N2222.
This setup affects how bright the LED glows.
Base Current of BC547 IB:
IB = VPot−VBE(BC547) / RPot
where,
- VPot is voltage from potentiometer (can move from 0 to 5V)
- VBE (BC547) is about 0.7V (base to emitter voltage)
- RPot is the resistance of potentiometer (like 1k ohm)
All these small calculations help to understand how circuit work.
Depending on real components and values numbers can change so always test and adjust.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Adjustable LED Dimmer Circuit following are the steps one should follow for connection:
Get All Parts:
- First collect all needed parts listed in the above circuit diagram.
Prepare Circuit Design:
- Plan how to put parts on breadboard or PCB.
- Leave enough space for LED display and the 2 potentiometers.
Connect Transistors:
- Put transistors in place like in diagram.
- Transistor T1 is used to control current going to LED.
Add Resistor:
- Add resistor in series with LED display.
- This resistor helps to stop too much current.
- Value depends on LED and how much current one want.
Put Potentiometers:
- Connect both potentiometers.
- P1 is for big adjustment and P2 is for small fine tuning of brightness.
Wire LED Display:
- Connect LED segment display to rest of circuit.
- Be careful with + and − side (polarity).
Heat Sink for T1:
- If circuit use much current than T1 transistor can get hot.
- Put heat sink on it to keep it cool.
Power the Circuit:
- Now connect power supply to the circuit.
Test the Circuit:
- Turn ON power.
- Start with potentiometers at low level and than slowly turn them to see LED to get brighter.
Make Adjustments:
- Turn potentiometers more to get just the right brightness.
Stay Safe:
- Be sure voltage and current is not too high.
- This stops damage or overheating.
Note:
- Always double check the wiring.
- If one is not sure about anything ask someone who knows electronics or get expert help.
Conclusion:
A Simple Adjustable LED Dimmer Circuit gives us more control on LED light.
We can change brightness how one wants and so it work good for many different lighting needs.
Leave a Reply