This is one TV, Video Transmitter Circuit It can send video from DVD, camera, or other device to old TV in our house.
We do not need big parts or hard things.
Just small circuit and little care is all we need.
This type of circuit is good for fun or learning.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Component | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified | |
| 470Ω | 1 | |
| 100Ω | 1 | |
| 4.7k | 2 | |
| Preset 470Ω | 1 | |
| Capacitors | ||
| Ceramic 3.3pF | 1 | |
| Ceramic 2pF | 1 | |
| Ceramic 10pF | 1 | |
| Ceramic 100nF | 2 | |
| Electrolytic 100μF 16V | 2 | |
| Semiconductors | ||
| Transistor BFR91A | 1 | |
| Inductor Coil, air core, 2 turns, 3mm diameter using 0.5mm thick super enameled copper wire | 1 |
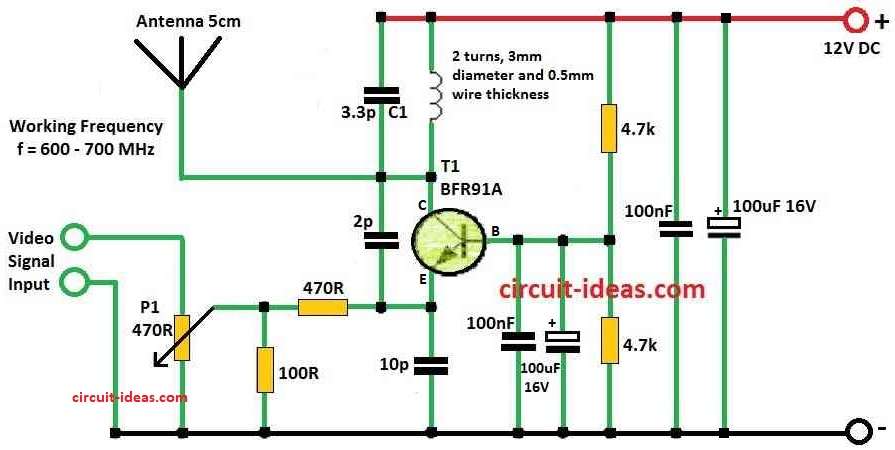
The main part of TV transmitter is small oscillator with high-frequency NPN transistor like BFR90, BFR91A, BFR92, or BFR93.
The transistor is small TO50 type.
It makes high-frequency waves and works as active part.
The LC circuit has one coil and capacitor C1 and these set frequency.
Change coil and C1 to pick UHF frequency from 470 to 855 MHz.
This makes circuit send signal on one TV channel.
Antenna is simple 5 cm wire which is connected direct to oscillator to send RF signal in air.
Oscillator wave carrier changes by video from camera or other source.
Wave gets strong or weak and this is amplitude modulation.
Circuit uses 5 to 12V power and when is power ON then oscillator sends RF signal.
Potentiometer P1 controls how much video changes wave like modulation depth.
Adjust P1 to get better picture.
After power is ON connect video source and turn coil or parts by hand to tune.
Use old analog TV to find signal on UHF channel which usually is about 37 to 50 means 600 to 700 MHz which is tuning.
Formulas:
Here are easy formulas for TV Video Transmitter Circuit:
This circuit use LC formula to find frequency.
Resonant frequency (f) is:
f = 1 / 2π√LC
where:
- f is the working frequency of transmitter
- π is around 3.14159
- L is coil value is the inductance
- C is capacitor C1 value in capacitance
We can choose L and C value using circuit diagram to get right frequency.
This tell what channel our transmitter will work on.
This formulas help explain how frequency and modulation work in TV transmitter.
How to Build:
To build a TV, Video Transmitter Circuit following steps are required for connections:
- For coil and capacitor C1 values look at the circuit diagram and these two parts decide what frequency transmitter will use.
- Change coil and C1 to get frequency in UHF range from 470 to 855 MHz.
- For antenna just connect a wire about 5 cm means 2 inch long straight to oscillator.
- Give power to transmitter using 5 to 12V supply.
- Make live wires short to stop too much inductance and capacitance.
- To stop unwanted signals from parasitic effect put 100nF capacitor close to transistor.
- Also use 100uF electrolytic capacitors in parallel to block noise from 50 Hz to hundreds of MHz.
Caution:
- Know the legal rules before using UHF TV band for sending signal.
- In some countries this kind of broadcasting is not allowed.
- If someone has legal trouble from using this it is not writers fault.
- Do this project only under its countries laws and try it at ones own risk.
Conclusion:
TV, Video Transmitter Circuit design can change based on what we need or want to do.
There are also ready made transmitters for sale and these have sound, more channels, different frequencies and stronger signal.
Before using always check the local rules about radio frequency broadcasting.
Leave a Reply