Simple Sawtooth Wave Generator Circuit is used in oscilloscope, TV, function generator and PWM.
IC 555 is very common and is easy to make sawtooth.
Voltage goes up slow and drop fast in sawtooth shape.
Frequency changes with potentiometer.
Circuit works with 5V to 15V.
Circuit Working:
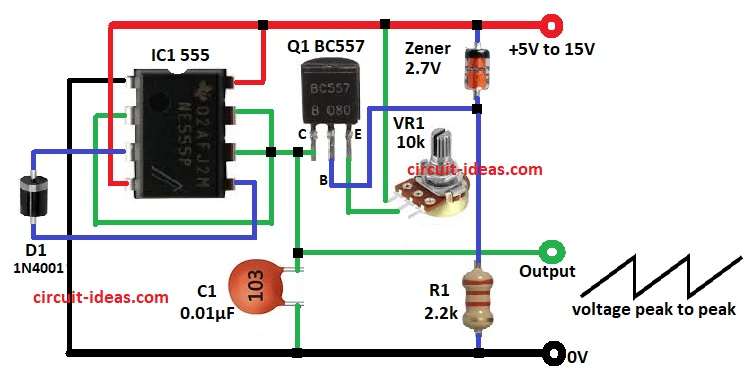
Parts List:
| Component | Value/Part Number | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 2.2k 1/4 watt | 1 |
| Potentiometer 10k | 1 | |
| Capacitor | 0.01µF Ceramic | 1 |
| Semiconductors | IC 555 | 1 |
| Transistor BC557 | 1 | |
| Zener Diode 2.7V | 1 | |
| Diode 1N4001 | 1 |
This above circuit uses 555 timer in special way to make sawtooth wave.
C1 charge through VR1 and PNP transistor BC557.
Transistor give steady current with smooth upward slope.
When C1 reach 2/3 supply voltage then 555 discharge fast with a sharp drop.
Cycle repeat with a constant sawtooth output.
Formulas with Calculations:
Below are the formulas with calculations for Simple Sawtooth Wave Generator Circuit:
Formulas for simple sawtooth wave circuit:
I = (V_Zener − V_BE) / VR1
= (2.7 − 0.7) / 10k
= 0.2 mA
Capacitor voltage rise:
V_C = I × (t / C)
I = 0.426 mA, C = 0.01 µF
Frequency:
f = 1 / (0.031 × V_CC)
V_CC = 12V
f = 2.7 kHz
How to Build:
To build a Simple Sawtooth Wave Generator Circuit follow the below mentioned steps for connections:
- Connect all parts as in diagram.
- Connect pin 1 of 555 to GND.
- Connect pin 2 to pin 6 and pin 7.
- Connect pin 3 to pin 5 through diode D1.
- Connect pin 4 and pin 8 to positive supply from 5V to 15V.
- Connect the emitter of transistor Q1 to positive supply.
- Connect the collector of Q1 to pins 2, 6 and 7.
- Connect the base of Q1 between the anode of the Zener diode and one end of resistor R1.
- Connect the other end of resistor R1 to GND.
- Connect the cathode of the Zener diode to positive supply.
- Connect one side of capacitor C1 to pins 2, 6, and 7 and the other side of C1 to GND.
- Check the sawtooth waveform across C1 using an oscilloscope.
Conclusion:
This Simple Sawtooth Wave Generator Circuit produces a sawtooth waveform using a 555 timer IC.
The PNP transistor with a Zener diode ensures a smooth rising slope.
Frequency can be changed by adjusting the capacitor, resistor or potentiometer.
References:
Operating principles of a sawtooth wave generator bootstrap circuit
Leave a Reply