A phone transmitter circuit is a bug transmitter circuit designed to convert sound waves from your phone conversation into electrical signal that can be transmitted over long distances.
These circuits are typically used in landline telephones.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Category | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 10k, 47k, 330Ω (1/4 watt each) | 1 each |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 47pF | 3 |
| Semiconductors | Transistor BC547 | 1 |
| Diodes | 1N4148 | 4 |
| Inductor | Coil inductor, 7 turns using 0.5mm wire, 3mm dia. | 1 |
This device is designed to capture audio from a phone conversation.
It then converts that audio signal into a format compatible with certain electronic devices.
The operational range is limited to a short distance and it utilizes the phone line itself as the transmitting antenna.
Following are the working details of the circuit.
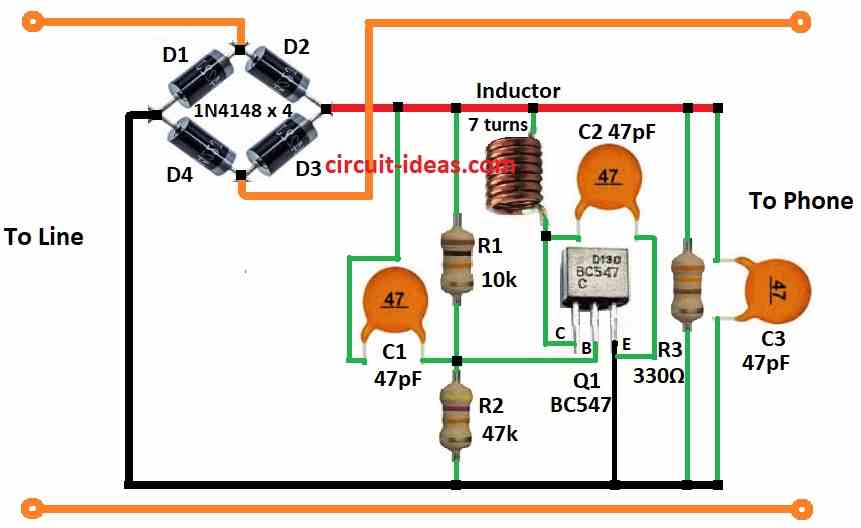
The four diodes D1 to D4 form a bridge rectifier that converts the AC voltage from the phone line into DC voltage to power the circuit.
Transistor Q1, along with R1, C1 and the coil form a colpitts oscillator circuit.
This circuit generates a high frequency carrier signal at the resonant frequency of the tank circuit determined by the coil and C1.
Capacitor C2 couples the audio signal from the phone line into the base of transistor Q1.
This causes the audio signal to modulate the carrier signal from the oscillator circuit.
The modulated signal is amplified by transistor Q1 and the tuned circuit before being transmitted.
Capacitor C3 allows for fine tuning the transmission frequency.
Formulas:
A colpitts oscillator circuit is formed by transistor Q1, R1, C1 and the coil L1 from the above diagram.
The essential formula for this colpitts oscillators resonant frequency f is as follows:
f = 1 / (2π * √(L1 * (C1 + C2)))
where,
- In hertz Hz f represents the resonant frequency.
- The coils inductance, expressed in henrys H is L1.
- The capacitance of capacitor C1 in farads F is denoted by C1.
- The capacitance of capacitor C2 in farads F is denoted by C2.
Note:
This formula assumes perfect components and ignores losses due to coil resistance or component tolerances.
These variables may cause the real oscillation frequency to slightly differ from the computed value.
You may need to utilize SPICE simulation or take into account the influence of the transistors base capacitance on the overall capacitance in order to obtain a more accurate estimation of the oscillator frequency.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Phone Transmitter Circuit follow the below mentioned steps for connections:
- Connect the collector of transistor Q1 to positive supply through inductor coil.
- Connect the base of transistor Q1 to capacitor C1.
- Connect the emitter of transistor Q1 to ground.
- Connect two resistors R1 and R2 in series from positive supply to negative supply.
- Connect capacitor C2 one end to inductor coil and other end to emitter of transistor Q1
- Connect capacitor C3 from positive supply to negative supply.
- Connect a resistor R3 from positive supply to negative supply.
Caution Note:
- It is important to be aware of local regulations regarding radio transmission devices.
- Operating such a device without a proper license might be illegal.
Conclusion:
Phone transmitter circuit play a crucial role in converting voice signals into electrical signals for transmission.
However, it is important to distinguish them from circuits designed to transmit phone conversation as radio signals.
Leave a Reply