Digitally Controlled Adjustable Voltage Regulator Circuit is made to give change output voltage for different use.
IC LM317 popular regulator and give output 1.25V to 37V adjustable.
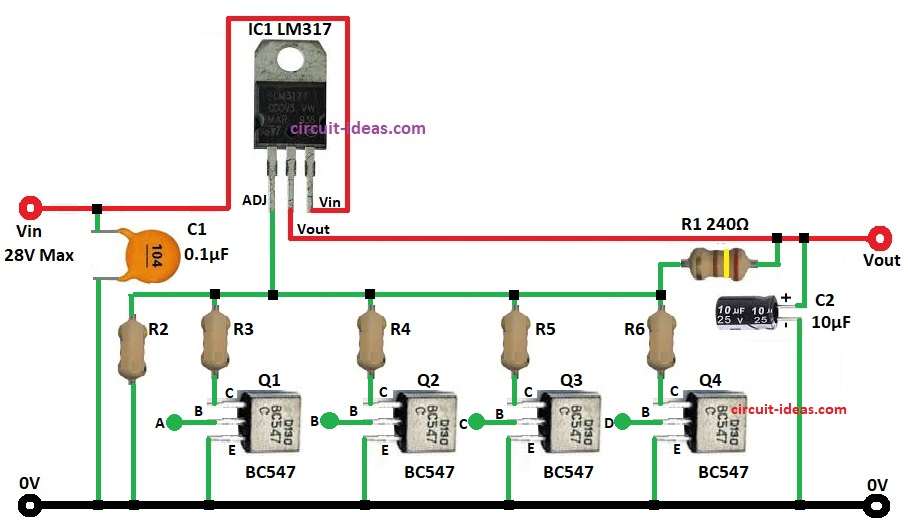
In this circuit LM317 IC work with digital control transistors and let user choose voltage easy.
It is good for different voltage need like microcontroller, power supply and for test tools.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Component Type | Value | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 240Ω 1/4 watt | 1 |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 0.1µF | 1 |
| Electrolytic 10µF | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | IC LM317 | 1 |
| Transistor BC547 | 4 |
IC LM317 is special device with three parts.
It keep steady 1.25V between output and adjust pin.
To get wanted voltage and use resistors which are connected to output, adjust pin and ground.
Here resistors R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 make different voltage levels.
Transistors Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4 act like switches.
When transistor is ON it connect resistor to circuit and change output voltage.
Output voltage formula for R2 to R6 is:
V_out = 1.25V × (1 + (R_set / R3)) + I_adj × R_set
Formulas with Calculations:
Formulas for Digital Adjustable Voltage Regulator:
V_out = 1.25V × (1 + (R_set / R3)) + I_adj × R_set
here,
- R_set is the resistor from R2, R3, R4, R5, or R6
- R3 is the fixed 240Ω resistor
- I_adj is the small current
So,
V_out = 1.25V × (1 + (R_set / 240Ω))
Example: If R_set = 1kΩ,
V_out = 1.25V × (1 + 1000/240) = 6.46V
Different R_set gives different output voltage.
How to Build:
To build a Digitally Controlled Adjustable Voltage Regulator Circuit follow the below mentioned steps:
- Put all parts as circuit show.
- Connect IC1 ADJ pin 1 to resistor divider between R5 and R6.
- Connect IC1 OUTPUT pin 2 to Vout regulated voltage.
- Connect IC1 INPUT pin 3 to Vin input voltage.
- Connect Q1 to Q4 collector pins to resistors R3 to R6 as per formula.
- Connect Q1 to Q4 base to digital control inputs A, B, C, D.
- Connect Q1 to Q4 emitter to ground.
- Connect resistor R2 from junction of R3 and ground.
- Connect resistor R1 between OUTPUT pin 2 and resistor R6.
- Connect capacitor C1 from INPUT pin 3 to ground.
- Connect capacitor C2 positive to OUTPUT pin 2 and negative to ground.
Conclusion:
This Digitally Controlled Adjustable Voltage Regulator Circuit uses IC LM317 to work good.
User select output voltage by turning ON the transistors.
This circuit is good for projects need different voltages like embedded system, test tools and for DIY power supply.
References:
Adjustable/Programmable Voltage Regulators – Linear, Low Drop Out (LDO) Regulators
Leave a Reply