Analog circuit is heart of electronics.
It works with continuous signals, not digital ON/OFF.
Everyday devices use radios, amplifiers, sensors and more.
Simple analog circuit helps us understand how signal change with time.
This article, Learn the Basics of Analog Circuits is good for beginners.
Working of Analog Circuit:
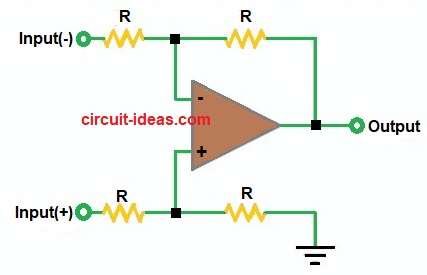
Circuit Parts used in for Analog Circuits:
| Component | Function / Description |
|---|---|
| Resistor (R) | Controls current and voltage levels in the circuit. |
| Capacitor (C) | Stores electrical charge and filters unwanted noise. |
| Transistor | Works as an amplifier or a switch. |
| Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) | Boosts weak input signals to higher levels. |
| Diode | Allows current to flow in one direction only. |
| Power Supply | Provides the required voltage and power to run the circuit. |
In the above diagram the op-amp takes two inputs with positive and negative.
Resistors balance both inputs.
Output depends on difference between inputs.
If Input(+) is bigger then Output is positive.
If Input(–) is bigger then Output is negative.
So, it amplifies difference which is called differential amplifier.
Two Main Types of Analog Circuits are:
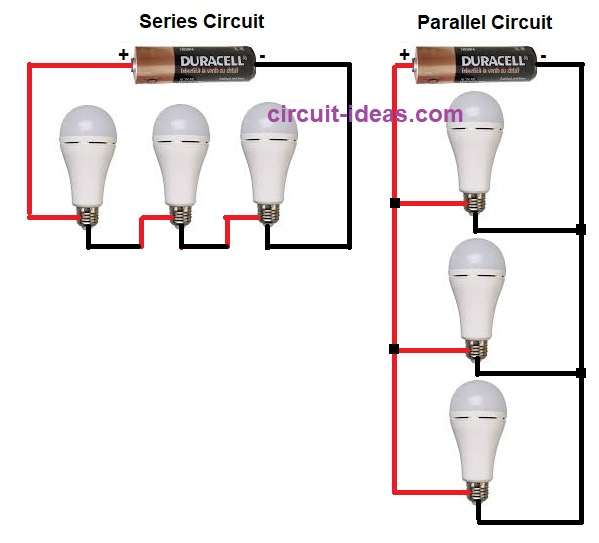
Series Circuit:
- Current same through all parts.
- If one part breaks then all stop working.
Parallel Circuit:
- Voltage same across all parts.
- If one part fails then others still work.
Difference Between Analog Signal and Digital Signal:
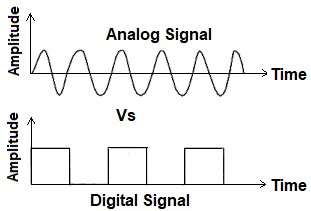
| Feature | Analog Signal | Digital Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Continuous wave | Discrete steps (0 and 1) |
| Value | Infinite values | Limited values |
| Noise | Affected by noise | Less noise |
| Example | Sound, temperature | Computer data, binary code |
Types of Analog Circuit:
Below is the diagram chart showing for a family tree of analog circuits:
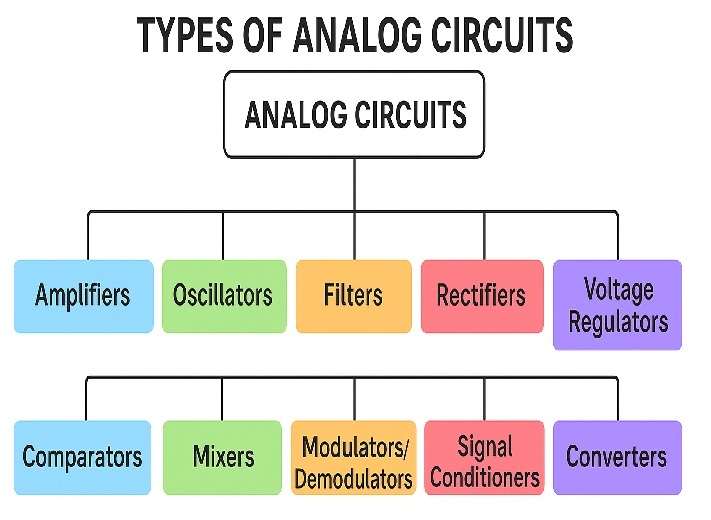
| Category | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Amplifiers | Increases the strength (amplitude) of a weak signal. | Op-amp amplifier, transistor amplifier, instrumentation amplifier |
| Oscillators | Generate continuous waveforms (sine, square and triangular). | RC oscillator, LC oscillator, Wien bridge oscillator |
| Filters | Remove unwanted frequencies from a signal. | Low-pass, High-pass, Band-pass, Notch filter |
| Rectifiers | Convert AC to DC current. | Half-wave rectifier, Full-wave rectifier, Bridge rectifier |
| Voltage Regulators | Maintain constant output voltage. | Zener regulator, IC 7805 regulator |
| Comparators | Compare two voltages and output a digital-like signal. | Op-amp comparator, zero-crossing detector |
| Mixers | Combine multiple signals into one. | Audio mixer, RF mixer |
| Modulators/Demodulators | Modify or recover signal for communication. | AM, FM, PM circuits |
| Signal Conditioners | Prepare sensor signals for processing. | Level shifters, filters, amplifiers |
| Converters | Change one signal type to another. | Analog-to-digital (ADC), Digital-to-analog (DAC) |
Applications of Analog Circuits:
- Audio amplifiers
- Radio and TV circuits
- Sensor signal processing
- Communication systems
- Measurement instruments
Conclusion:
Learn the Basics of Analog Circuits are the foundation of all electronics.
They deal with real-world signals smoothly.
Even today, analog and digital work together in smart devices.
Learning analog is first step to mastering electronics.