This article tell how to use simple parts like transistor, capacitor and diode to make Simple Delay Timer Circuit.
This timer can wait some time like few seconds or minutes before turning something ON.
This kind of delay timer is needed in many circuits so things happen in correct order.
What is a delay timer circuit:
Device that uses relay to make delay before turn ON something like appliance then this is called delay timer circuit.
Why Delay Timers are Important:
- In many electric works using delay for few seconds or minutes is good to make circuit work better.
- If no delay is used then circuit can get damage or will not work right.
How It is Made:
- We need to join transistor and some simple parts to make delay happen.
- We can see this in circuit diagram below.
Parts Used for Delay Timer:
- Transistor stop too much current by using one small base resistor.
- Relay work like a load on transistors collector side.
- After the base resistor one more part is there it is capacitor which is very important for delay.
Circuit Working:
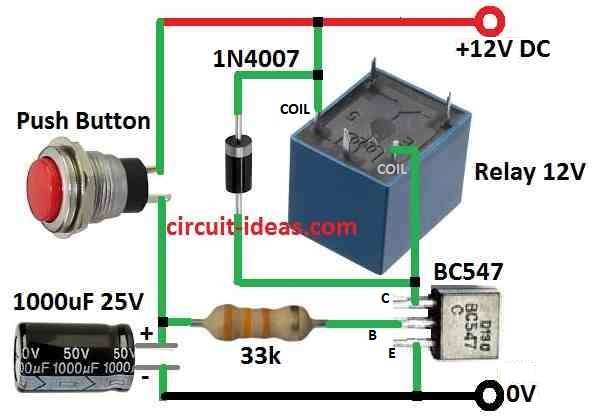
Parts List:
| Component Type | Component Details | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 33k 1/4 W CFR | 1 |
| Capacitor | Electrolytic 1000µF 25V | 1 |
| Semiconductors | Transistor BC547 | 1 |
| Diode 1N4007 | 1 | |
| Relay 12V | 1 | |
| Push button | 1 |
How Circuit Work:
When push button is pressed power goes through base resistor and this turn ON transistor and relay.
At same time capacitor also start charging full.
After button is released transistor still stays ON for some time.
It uses power stored in capacitor which then capacitor start losing charge means it gets discharge.
Relay is not turn ON until capacitor is fully empty.
How long transistor stay ON depends on size of capacitor.
Bigger capacitor = more time delay.
Base resistor also changes the delay.
Bigger resistor = transistor stay ON longer after button is released.
Formulas and Calculations:
Formulas for Simple Delay Timer Circuit:
We connect RC delay part to transistor base to find time delay (τ) of circuit.
We use this formula to find time constant:
τ = R × C
where:
- τ (tau) is time constant in seconds (s)
- R is resistor value in ohms (Ω)
- C is capacitor value in farads (F)
How to Calculate:
Step 1 Change capacitor to farads:
Example:
1000µF = 1000 × 10⁻⁶ F = 0.001 F
Step 2 Find time constant:
Use values in formula:
τ = 33,000Ω × 0.001F = 33 seconds
What It Means:
With these parts the circuit gives around 33 second delay from input change to output from transistor collectors change.
Note:
This number is just close idea.
Actual delay can change little because of transistor behavior and small leakage currents.
Time constant (τ) means how long it take for capacitor voltage to reach around 63% of final voltage.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Delay Timer Circuit using a single transistor and a push button then follow the below mentioned steps:
Transistor Setup:
- Connect transistor collector to positive supply of PCB.
- Connect emitter to negative GND side of PCB.
Base Resistor Connection:
- One side of base resistor connects to transistor base.
- Other side of resistor connect to one side of push button.
Capacitor Connection:
- Connect positive longer leg of capacitor to other side of push button.
- Negative short leg of capacitor connect to negative supply of PCB.
Relay Connection:
- Connect relay coil pins between transistor collector and positive supply.
- Positive wire of power supply connect to PCBs positive line.
- Negative wire connect to PCBs negative GND
- Press the push button for few seconds.
- See the relay turn ON.
- Release the button and relay stay ON for some time depending on capacitor.
Modifications:
- To change delay time try bigger or smaller capacitor.
- We can also try different base resistor to change how long transistor stays ON.
Extra Tip:
- If we want longer delay try using two transistors in series for dual stage.
- This make circuit more sensitive and let us use bigger resistors for more time.
- Before turning ON check twice all wires, polarities and component values to avoid mistake.
Conclusion:
These ideas help electronics hobby people to build a Simple Delay Timer Circuit that can be changed for different needs.
Try different parts and learn how delay change.
It is good for learning and making custom projects.
Leave a Reply