We can make simple Water Level Controller Circuit using IC 555 for our tank.
It stop pump when tank is full and start again when water is low.
We can change some parts to match our tank size and water level.
Circuit Working:
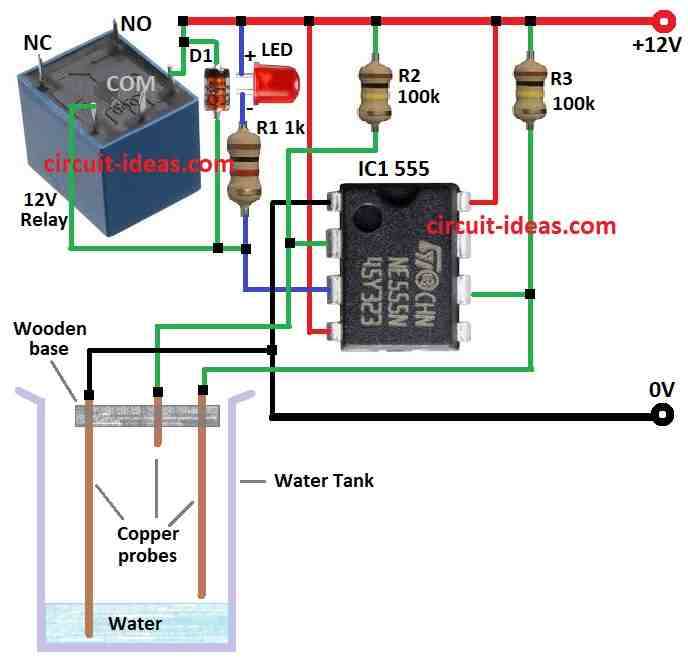
Parts List:
| Category | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 1k 1/4 watt | 1 |
| 100k 1/4 watt | 2 | |
| Semiconductors | IC 555 | 1 |
| LEDs any 5mm 20mA | 1 | |
| Diode 1N4148 (D1) | 1 | |
| 12V Relay | 1 | |
| Water Tank | 1 | |
| Copper probes | 3 |
This circuit is cheap because it uses easy parts.
Because of 100k resistors, pins 2 and 6 show voltage even when water does not touch the probes.
When water touches the probes then there is no voltage at these pins.
Pins 2 and 6 just check 1/3 and 2/3 of power.
They only see voltage or no voltage.
Pin 2 is LOW then pin 6 goes HIGH means normal.
Pin 2 is HIGH means nothing happens.
Pin 6 is LOW means nothing happen.
Water LOW means pins 2 and 6 HIGH and output pin 3 is LOW.
Water goes up and output remains same then chip wait until pin 2 goes LOW.
When water reaches pin 2 and pin 2 is not HIGH then output goes HIGH and pump stops.
Water drop and pin 2 is HIGH then nothing happens.
Water drop more then pin 2 is not LOW and pin 6 HIGH and output goes LOW and pump start.
Safety Tips:
- Be careful when working with electricity.
- Use correct parts and right voltage rating.
- Know basic electronics before doing this.
Conclusion:
We can use 555 IC to make DIY Water Level Controller Circuit.
It fills tank and stops overflow using pump, probes and timer output.
This circuit is cheap and useful but safety and correct setup is important.
Leave a Reply