One may believe that a multimeter are used to test any electrical device, however this may not be always safe with semiconductors.
This article explains how to construct a simple harmless tester designed especially for semiconductors.
To test several semiconductor types this tester is simple to construct and uses a safe current level.
What is a Tester Probe Circuit:
The tester probe circuit is a handy measurement and testing tool which is used to quickly find out the functioning of an electrical circuit.
Also it is used to ensure that particular electrical equipment and components are in good operating condition.
Circuit Working:
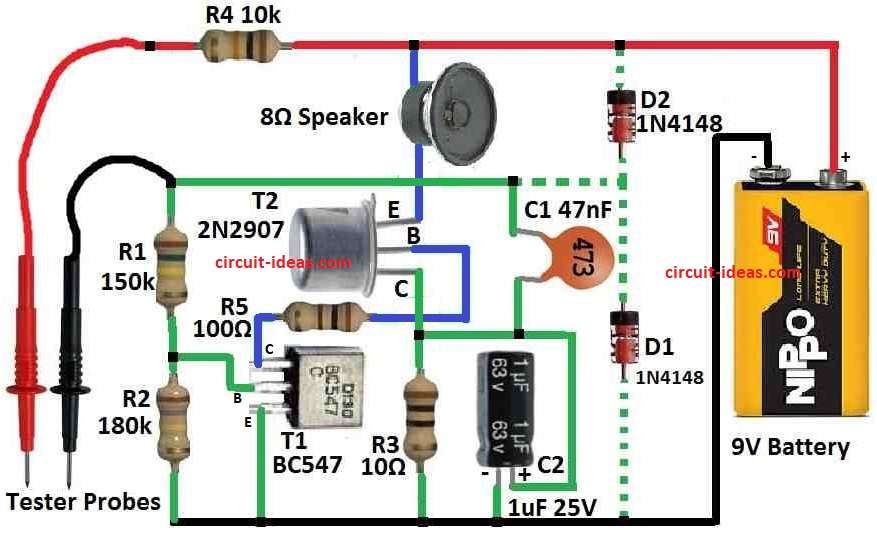
Parts List:
| Category | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 150k CFR 1/4 W | 1 |
| 180k CFR 1/4 W | 1 | |
| 10Ω CFR 1/4 W | 1 | |
| 10k CFR 1/4 W | 1 | |
| 100Ω CFR 1/4 W | 1 | |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 47nF | 1 |
| Electrolytic 1µF 25V | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | Transistors BC547 | 1 |
| Transistors 2N2907 | 1 | |
| Diodes 1N4148 (optional) | 2 | |
| Speaker 8Ω | 1 | |
| Battery 9V | 1 | |
| Tester probes red | 1 | |
| Tester probes black | 1 |
T1 and T2 form a voltage controlled LF oscillator.
The loudspeaker acts as a load in the oscillator circuit.
The oscillator frequency is calculated by C1, R1, R4 and the external resistance between the measuring leads.
Resistor R3 serves as the collector resistance of T2 and C2 acts as low frequency decoupling for this resistor.
Oscillator Operation:
The oscillator frequency is adjusted for testing purposes.
There is no need to keep looking at the testing devices because the loudspeaker offers a sound throughout testing.
Safety Features:
The circuit makes sure that the device being tested is not harmed.
To keep the components of the tester safe from harm from the circuit being tested diodes D1 and D2 are included.
Power Efficiency:
When the testing probes are not electrically connected the circuit consumes very little current.
A longer battery life that is about equal to the batteries shelf life is ensured by this design.
Formulas:
The oscillation frequency (f) and the time constants related with these charging and discharging cycles have an equal correlation:
f = 1 / (Tcharge + Tdischarge)
where,
- The charging time constant or Tcharge is dependent on R and C.
- The discharging time constant Tdischarge is dependent on R and C during the discharging process.
Investigation of Tools:
However it is possible to carry out a comprehensive research of the circuit to identify the elements affecting the frequency and to calculate its range:
Charging Phase:
When the voltage across capacitor C decreases one BJT activates allowing the capacitor to charge along a particular path indicated by the resistors.
The charging rate is decided by the charging current and the resistance value.
Discharging Phase:
When the capacitor reaches a certain voltage threshold the BJT changes features and turns off.
The capacitor can discharge into a second channel created by a fresh pair of resistors.
The discharge rate is also affected by the resistance that is present.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Tester Probe Circuit follow the below mentioned connections steps:
- T1 and T2 should be connected in the manner described.
- The circuit must include resistors R1, R3 and R4.
- Capacitors C1 and C2 must be added for decoupling and frequency control.
- Add diodes D1 and D2 for protection against possible harm.
- In the oscillator circuit connect the loudspeaker as the load.
- To ensure precise testing make sure the measurement leads are connected properly.
How to test:
Below mentioned are the few methods for testing the Tester Probe Circuit:
- To use the semiconductor tester make sure the battery is inserted into the circuit correctly.
Connect Measuring Leads:
- Connect the measuring leads to the proper circuit spots.
- Before connecting to the semiconductor or IC be sure that the testing probes are not electrically connected.
Identify Test Points:
- Choose the spot to test on the IC or semiconductor that one wish to examine.
- To find out which test points are suitable check the components datasheet.
Touch Test Points:
- Use measuring leads to gently touch the chosen test spots on the semiconductor or IC.
- To confirm that the circuit is working the loudspeaker needs to produce a sound.
Listen for Indication:
- See whether the loudspeakers audio indicator changes in tone or strength.
- This variation is used to identify various states or properties of the semiconductor that is being tested.
Disconnect and Repeat:
- After testing one set of test points disconnect the measuring leads and repeat the process for other test points on the semiconductor or IC.
Verify Results:
- Check the results against the requirements or features of the IC or semiconductor during testing.
- Confirm that the noticed signals match to the expected behavior..
Turn Off:
- When testing is over turn OFF the semiconductor tester to save battery life.
Conclusion:
This do-it-yourself method provides an accurate method to do silent testing without running the risk of damaging the circuit while being tested.
Leave a Reply