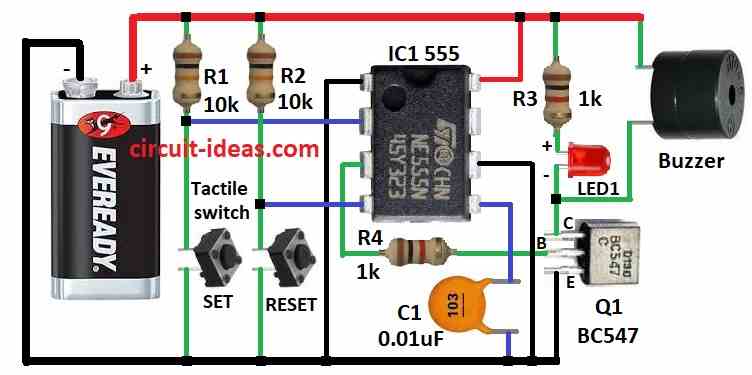
Building an inexpensive and simple alarm system is made possible by utilizing the IC 555 in a basic panic alarm button circuit.
The IC 555 has two stable states alarm on and alarm off because it is designed as a bistable circuit.
When the panic button is pressed, the timer starts and it continues to run until the reset button is touched.
The timers high output signal triggers the transistor, which in turn lights the LED and buzzer to sound the alarm.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Category | Item | Quantity | Power Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 10k | 2 | 1/4 watt |
| 1k | 2 | 1/4 watt | |
| Capacitors | 0.01μF | 1 | – |
| Semiconductors | IC 555 | 1 | – |
| Transistor BC547 | 1 | – | |
| Tactile switches | 2 | – | |
| LED (red) 5mm 20mA | 1 | – | |
| Buzzer | 1 | – | |
| 9V Battery | 1 | – |
This implies that when it is activated, it will keep oscillating and provide a continuous output signal.
Timing resistors R1 and R2 and capacitor C1 in this circuit establish the oscillation frequency, which regulates when the alarm goes off.
How the circuit works:
The circuit is in a stable condition when power is provided, and the IC 555s output pin 3 is low.
The buzzer and LED are off, and the transistor BC547 is off since there is no voltage signal applied to its base pin.
The IC 555s pin 2 trigger can be briefly connected to ground by pressing the usually open push button SET.
This starts the oscillation of the timer, which makes the output pin 3 go high.
Since current may now pass via the transistors base collector pin, the transistor BC547 is turned on by the high output from pin 3 of the IC 555.
The buzzer and LED are linked to the positive side of the transistors collector, which permits current to pass through them and sound the warning.
The IC 555s pin 4 reset is linked to the usually closed push button RESET in a way that causes it to automatically send a high voltage signal.
This keeps the alarm off and the timer reset.
However, when you push the reset button, pin 4 is briefly disconnected from the high voltage, which resets the IC 555 and lowers pin 3s output.
The alert ceases as the output falls, this causes the transistor to shut off.
Formulas:
The following are the main equations and factors to take into account while creating a set reset SR configuration for an IC 555 in a panic alarm button circuit:
Triggering Resistor Formula Rtrigger:
To guarantee steady triggering of the IC 555 and debounce the panic alarm button, the resistor Rtrigger is employed.
Rtrigger (typical range)=1k to 10k
- Its value is determined by the buttons attributes and the preferred triggering sensitivity.
Timing resistor formula (R1 and R2):
The time delay for the alarm to sound and go off after the panic button is hit is adjusted using R1 and R2.
The following formula can be used to approximate the temporal interval T for each state:
T = 0.693 × (R1+R2) × C
where,
- R1 and R2 are in ohms Ω.
- C is in farads F.
Note:
This circuit illustrates how the Panic Alarm Button Circuit is implemented simply utilizing an IC 555 configured in a set reset mode.
To get the appropriate time for the activation and deactivation of the alarm, adjust the values of the resistor and capacitor.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Panic Alarm Button Circuit using IC 555 follow the below mentioned steps for connections:
- Assemble all the required components, as mentioned in the above circuit diagram.
- Connect pin 1 of IC 555 to ground.
- Connect pin 2 of IC 555 between resistor R1 and SET tactile switch.
- Connect pin 3 of IC 555 to base of transistor Q1 through resistor R4.
- Connect pin 4 of IC 555 between resistor R2 and RESET tactile switch.
- Connect pin 5 of IC 555 to ground through capacitor C1.
- Connect pin 6 of IC 555 to ground.
- Connect pin 8 of IC 555 to positive supply 9V battery.
- Connect transistor Q1 collector to positive supply through resistor R3 and LED1, connect base of transistor Q1 to pin 3 of IC 555, connect emitter of transistor Q1 to ground.
- Connect buzzer one end to positive supply and other end between collector of transistor Q1 and LED1.
Safety Measures:
- In order to prevent short circuits or component damage, double check the wiring and component location.
- Make that the transistors, capacitors and resistors in the circuit are rated for the voltage and current that are being utilized.
- To prevent damage, make sure LEDs and electrolytic capacitors are positioned properly.
- Safe connections for dependable connections, make use of heat shrink tubing (if necessary) and appropriate soldering skills.
- To shield the circuit from moisture, dust and unintentional touch, think about enclosing it in a non conductive container.
Conclusion:
When the panic button is pressed, this simple panic alarm button circuit using IC 555 to produce an oscillating signal.
The alarm is produced by the transistor being activated by this signal, which also powers the buzzer and LED.
You may manually stop the alarm and reset the timer by pressing the reset button.
Leave a Reply