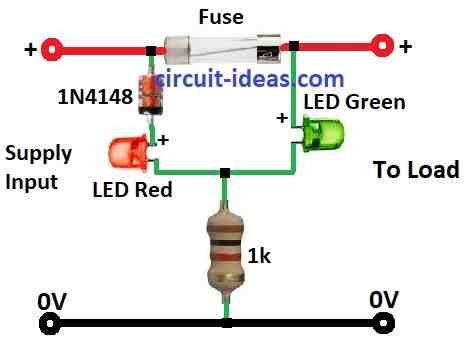
This Simplest Blown Fuse Indicator Circuit shows if fuse is good or bad without checking it by hand.
If fuse is okay then green LED turns ON.
If fuse blows then green LED goes OFF and red LED turns ON.
That means fuse is bad and needs to change.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Component | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | ||
| 1k 1/4 watt | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | ||
| Diode 1N4148 | 1 | |
| LED Red 5mm, 20mA | 1 | |
| LED Green 5mm,20mA | 1 | |
| Fuse | 1 |
This circuit uses two LEDs red and green and one diode to show if fuse is blown.
How it works:
When fuse is good then current flows normally.
Very small voltage drop across the fuse.
Most voltage goes through diode 1N4148 around 0.7V.
Red LED stays OFF because not enough voltage turn it ON.
Green LED gets full voltage and lights up.
If fuse blows:
Circuit opens with no current flow.
Voltage now drops across the blown fuse.
Red LED gets enough voltage and turns ON and shows fuse is bad.
Green LED gets no power and turns OFF.
Formulas:
From the circuit with LED green and red lights up depends on voltage drop across the resistor and LED.
Choosing Resistor:
We need to pick right resistor for green LED.
This depends on:
Supply voltage Vsupply
LED forward voltage VfLED
Desired current ILED
Use ohms law:
R = (Vsupply – VfLED) / ILED
where:
- VfLED is the forward voltage of green LED
- R is the resistor in ohms Ω
- Vsupply is the supply voltage in volts V
- ILED is the current through LED in amps A
Tips:
Check green LED datasheet for VfLED
Choose ILED within safe range usually from 10 to 20 mA
Try different resistor values or use online LED calculator
Check the LED lights are bright enough, but not with too much current.
How to Build:
To build a Simplest Blown Fuse Indicator Circuit we need to follow the below mentioned connections steps:
- Find positive and negative rows on PCB.
- Connect power supply (+) to positive row.
- Connect power supply (–) to negative row.
Place LEDs and Resistor:
- Put red and green LEDs on PCB and legs in different rows.
- Short legs cathodes of both LEDs should be on same side.
Connect Green LED:
- Solder long leg anode of green LED to same row as (+) supply.
Resistor Setup:
- Put 1k resistor near the short legs cathodes of LEDs.
- One leg of resistor goes with LED cathodes.
- Other leg of resistor goes to supply row.
Red LED Cathode:
- Short leg of red LED connects to resistor side.
Place Diode 1N4148:
- Put diode on PCB with band side cathode facing (+) supply.
- Band side goes to (+) supply row.
Connect Red LED Anode:
- Long leg anode of red LED connects to diodes non band side.
- Fuse Connection Important to Turn Power OFF:
Find two ends of the fuse.
- One end of fuse goes to (+) supply row.
- Other end goes to load side.
Testing ensure power is OFF first:
- Turn power ON.
- If fuse is good then green LED will light up.
- If fuse is blown then red LED will light up.
Safety Tips:
- Double check all connections before powering ON.
- Use 2 to 3V power for small LEDs.
- Do not touch live circuit.
- Ask expert if anyone is unsure about this project.
Conclusion:
This Simplest Blown Fuse Indicator Circuit shows fuse status like with green LED the fuse is OK and with red LED the fuse is blown.
This simple circuit shows fuse status using lights.
It helps in checking and fixing problems in electronics.
Leave a Reply