This post teaches how to make Simple 220V AC Light Dimmer Circuit for home lights.
With this dimmer we can make light more or less bright by turning off current slowly.
Working with high voltage is not safe.
Good electrician should fix this in house and only do if big person is watching.
New people should not try this.
What is AC Light Dimmer Circuit:
AC light dimmer is electric thing used to change how bright light is mostly for normal bulbs like incandescent type.
Main reason to use dimmer is to change power going to light so user can choose how much bright they want.
To do this voltage or current go to bulb is controlled so light become more or less.
Understanding Triac Dimmers:
Triacs used a lot in circuits to turn AC things ON or OFF.
They work when to get DC trigger from outside.
Mostly they are used for full ON or OFF but also are used where AC needs to be controlled.
Like in dimmer switch triac only work in some parts of AC wave.
And this makes output AC smaller than input AC.
Dimmer switch for normal light bulb is good example as it changes power to light so light become more or less bright.
Circuit Working:
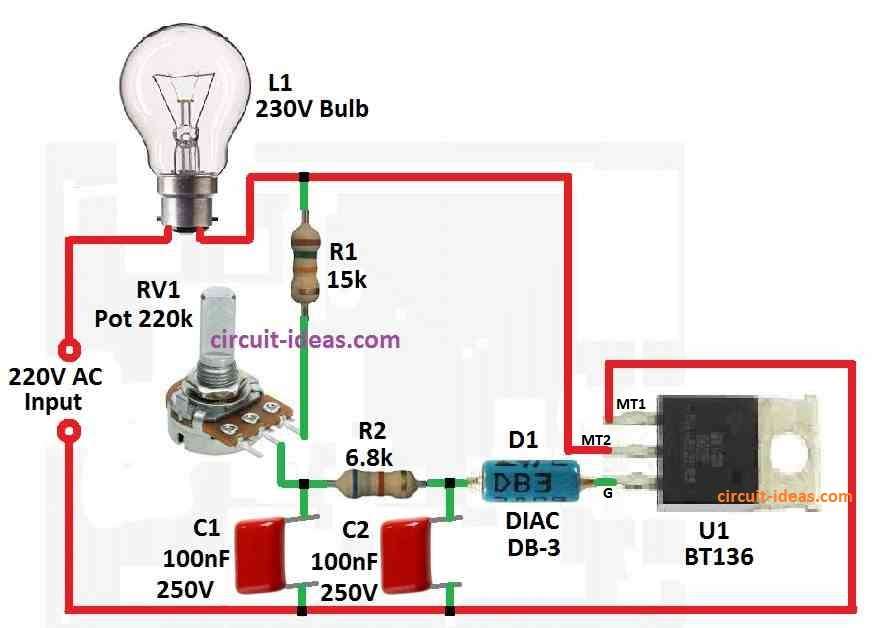
Parts List:
| Category | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 15k CFR, 6.8k CFR | 1 each |
| Potentiometer 220k | 1 | |
| Capacitors | PPC 100nF 250V | 2 |
| Semiconductors | Transistor BT136 | 1 |
| DIAC DB-3 | 1 | |
| Incandescent Bulb 230V | 1 |
When AC power goes in circuit after some time C2 get full charge.
Then diac gets enough voltage to start working.
When diac work triac also start to conduct.
But when this happen C2 loses charge and goes down below diac working level.
Because of this diac and triac stop again and this happen many times in each AC wave.
This make the light less bright because voltage goes down in a controlled way.
C1 is not needed for normal bulbs but is very important if using with things like motors or fans or like inductive loads.
Inductive loads send some power back so C2 charging breaks.
C1 help fix this problem which gives small power bursts to keep triac working even when C2 is empty.
While working these dimmers make lot of radio noise like RF noise.
So we need to add RC network to dimmer to reduce this noise and keep it clean.
Formulas:
Basic 220V AC Light Dimmer Circuit:
To make basic light dimmer for 220V AC we have used TRIAC, DIAC and some other parts.
This kind of circuit changes phase angle of AC voltage to control how much power goes to light bulb.
Time Calculation:
How long delay happen in phase control circuit is found using resistor and capacitor which is the RC network.
Time constant (𝜏 tau) tell us how much delay before TRIAC turn ON.
We use this formula to find delay angle (α):
α = 1 / 2πfRC
where:
- f is AC frequency in most places around 50 Hz.
- R is resistance with potentiometer + fixed resistor.
- C is total capacitor value for C1 and C2 in farads.
Each time AC cycle happens TRIAC turn ON at a certain angle.
We can turn the potentiometer to change this angle and this changes how bright the bulb becomes.
So by changing phase angle we make the bulb go dim or bright and this is how basic dimming works.
How to Build:
How to build a Simple 220V AC Light Dimmer Circuit is mentioned below:
Triac Connection:
- Connect MT1 pin of triac to a live wire from AC mains.
- Connect bulb the load to MT2 pin.
- Gate of triac connects through diac and connect where R1 and C2 meet.
- Or just connect like show in diagram.
Set Up Potentiometer:
- One side of potentiometer connect to point where R1 and C2 join.
- Other side connect to common point of load.
- Middle pin the wiper of potentiometer goes to AC neutral.
C1 Connection:
- If using inductive load then connect one side of C1 to point of R1 and C2.
- Other side of C1 goes in parallel with load.
Power Source:
- AC phase wire connect to triac MT1.
- Potentiometer middle pin wiper goes to AC neutral.
Ground Optional:
- For safety connect ground to circuit.
Testing and Changing:
- Turn ON power and check if bulb lights up.
- Turn potentiometer knob to make light more or less bright.
- Check if RF noise is less when RC network is added.
Safety Tips:
- Remember all circuits here are connected to AC mains.
- Be very careful when touching or testing especially when power is ON.
Conclusion:
If we follow steps properly and stay safe we can build a Simple 220V AC Light Dimmer Circuit by using a Triac
We can also change how bright the light bulb glows.
Leave a Reply