This circuit is Bench Power Supply Circuit which is easy to use and works good.
We can change voltage and see current.
What is a Bench Power Supply:
Bench power supply circuit be useful device which gives steady and control power for working in lab, workshop and testing electronics.
This circuits main job is give same voltage and current to circuits and devices when building, checking or fixing them.
Circuit Working:
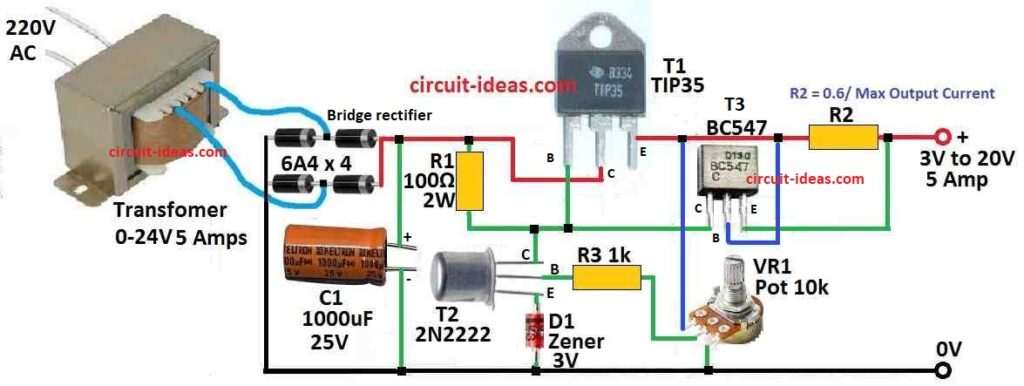
Parts List:
| Category | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 100Ω 2W | 1 |
| 1k | 1 | |
| R2 (calculated as 0.6 / max output current) | 1 | |
| Potentiometer 10k | 1 | |
| Capacitor | Electrolytic 1000µF 25V | 1 |
| Semiconductors | Transistors 2N2222, TIP35, BC547 | 1 each |
| Bridge diodes 6A4 | 4 | |
| Transformer 0-24V 5 Amps | 1 |
Transformer 24V 5A is used for power in this circuit.
Output from transformer connects to bridge rectifier to change AC to DC.
Then one big filter capacitor is put after rectifier to make DC smooth.
This smooth DC is around 30V which connects to power supply circuit.
TIP35 transistor is uses like emitter follower.
Its base connects straight to 30V input.
One 2N2222 transistor and one potentiometer makes feedback loop.
TIP35 emitter connects to base of 2N2222.
Potentiometer changes feedback so output voltage can be adjusted.
Zener diode is between emitter and ground of 2N2222 to keep voltage stable.
One resistor is put in TIP35 emitter line for current limit.
BC547 transistor also connect with this resistor and TIP35 base.
If too much current connect to load then BC547 stop it and acts like current limiter.
So 2N2222 and potentiometer controls the voltage.
BC547 controls the current and protect from overload.
Formulas and Calculations:
This design control the base voltage of transistor T1 and its control output voltage too.
It does this by changing voltage drop on resistor R1 and this drop happen mostly from current made by transistor T2.
Potentiometer VR1 connects one end to ground.
So when slider connects close to ground side then base current of T1 makes voltage drop on R1 and this turns OFF T2.
Output voltage at emitter of T1 is almost same as collector voltage with only little less:
VE = Vin – 0.7V
0.7V is normal drop between base and emitter of BJT like T1
So if input is 15V:
VE = 15 – 0.7 = 14.3V
Now when VR1 slider moves to high side of positive then T2 gets full emitter voltage from T1 and turns ON strong.
Then Zener diode D1 and resistor R1 get directly connected.
Lets say Zener voltage is Vz and base voltage of T1 become same like Vz.
So:
VE = Vz – 0.7V
Example: if Zener D1 is 6V then:
VE = 6 – 0.7 = 5.3V
This mean Zener voltage set the lowest output voltage when VR1 is at lowest point.
This method is simple and works good, but it is having one big problem it does not protect from short circuit.
If output accidentally shorted or current become too high then T1 transistor get hot fast and maybe gets burn.
But this problem can be fixed easily by adding current control.
How to Build:
To build a Bench Power Supply Circuit follow the below steps:
Power Supply Section:
- Connect transformer wires secondary side to bridge rectifier input.
- Then connect output of rectifier to one big filter capacitor to smooth the DC.
TIP35 Transistor:
- Connect emitter of TIP35 to positive power line.
- Collector of TIP35 connects to the load like resistor or circuit
- Base of TIP35 connect direct to 30V input.
Feedback Loop:
- Emitter of 2N2222 transistor connect to TIP35 output.
- Base of 2N2222 connect to point between potentiometer and resistor.
- Other end of resistor connects to emitter of TIP35.
- Collector of 2N2222 connects to positive power line.
- Zener diode connect between emitter and ground of 2N2222.
Current Limiting Section:
- Put one resistor in line with TIP35 emitter for current limit.
- Base of BC547 transistor connect to point between this resistor and TIP35 emitter.
- Collector of BC547 connects to positive power.
- Emitter of BC547 connect to TIP35 base.
Control:
- Middle pin wiper of potentiometer connects to base of 2N2222 transistor.
- One end of potentiometer connect to positive line.
- Turn potentiometer to adjust feedback and control output voltage.
Load Connection:
- Connect the load which is the resistor or circuit to TIP35 collector.
Heat Sink:
- TIP35 can get hot so use heat sink to keep it cool.
Extra Tips:
- Check connections two times and be sure positive and negative are correct.
- Use right resistor values for good feedback and current limit.
- We can add small capacitors or diodes for better stability and safety.
- Connect ground of circuit to ground of power supply.
Note:
- After building slowly turn potentiometer and check voltage change.
- Also test current limit by changing load.
- Be sure parts do not go over their max voltage or current rating.
Conclusion:
In this post BC547 stops too much current as it works like a safety switch.
Potentiometer with 2N2222 controls how much voltage comes out.
Together we can make Bench Power Supply Circuit that can adjust voltage and stop too much current.