Simple Full Duplex Audio Line Circuit is like a strong talking line.
Two people can talk at a same time on one wire like a phone call.
Not like a walkie talkie where only one person talk and other wait.
But with full duplex both people talk anytime like a actual talking.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Category | Part Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors (All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified) | 220k | 1 |
| 2.2k | 1 | |
| 200k | 1 | |
| 47k | 2 | |
| 100k | 6 | |
| Preset 10k | 1 | |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 0.27 µF | 2 |
| 2.2µF | 2 | |
| Trimmer 100pF | 1 | |
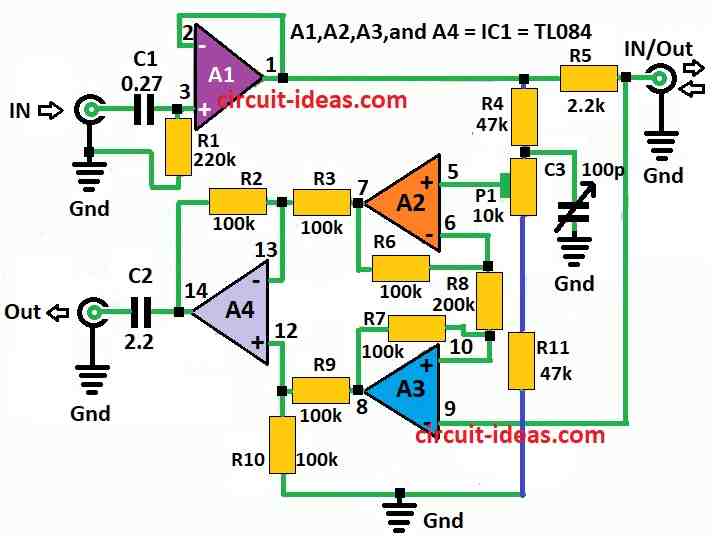
| Semiconductors | IC A1, A2, A3, A4 = IC1 TL084 | 1 |
Circuit working with simple and basic idea:
Two transmitters one on each side send signal through wire.
Voltage on wire is both signals added together like U1 + U2.
But in actual circuit it more like half that sum.
Each side takes out own signal and ignore the other one so both sides need same circuit.
Op amp A1 works like helper and it changes impedance and send signal.
Resistor R5 is like guard it protect A1 from other signal coming back from other side.
Signals mix together at output and this mix connects to op-amps A2, A3 and A4 and they work like brain to understand signal.
Right signal come out through divider R4, R11 and P1 and get picked from mixed signal at OUT.
To ensure bad signals i.e same phase are good but need very accurate resistors.
With good resistors noise goes down a lot like 80dB at 1kHz and 60dB at 20kHz.
If cable is long and noise is still there, then one can adjust C3 to make it better.
To set it up right first connect signal generator to IN and send 5kHz sine wave with 1V.
Then connect twisted pair wire to IN and OUT.
At the other end short the input of second circuit.
Next change signal to 10kHz and adjust C3 until one receives clear signal.
Formulas:
TL084 op-amp used in Full Duplex Audio Line Circuit.
It helps make two separate ways one for sound going IN and one for sound going OUT.
It keeps signal strong and clean and stops feedback noise.
TL084 is one chip with four op-amps inside.
People like it for sound circuits and it have got big bandwidth and low noise.
Full duplex means talk and listen at same time like phone call or walkie-talkie (but better one).
Some math to think about:
Regarding a non-inverting setup: G = 1+ Rf / Rin
For inverting configuration: G =−Rf / Rin
where,
- Rf is feedback resistor (connects around op-amp)
- Rin is input resistor (where signal connects IN)
Other things to check:
Choose right capacitors for filtering and blocking DC (AC coupling).
Pick parts to match sound frequency range like voice or music.
Important:
To make good two way sound with no noise, no echo need to follow:
- Set gain right
- Keep input/output separate
- Stop signals from mixing wrong
TL084 is good for this and it give clear and strong sound and works well in audio projects.
How to Build:
To build A Simple Full Duplex Audio Line Circuit following are the steps to follow:
Op -Amps Operational Amplifiers:
- Use op-amp like LM741 or other similar type.
Resistors:
- Pick low tolerance resistors as they work better and are more accurate.
Capacitor (C3):
- Use normal capacitor and can change value later to get best performance.
Twisted Pair Cable:
- Use twisted pair wire for sound signal which helps reduce noise.
- Use a signal generator to send test signal into the circuit.
How to Connect:
Op Amps (A1, A2, A3, A4):
- Follow the diagram to connect them right.
- Check the datasheet to know which pin do what.
Resistors (R4, R5, R11, P1):
- Connect them like shown in diagram.
- P1 is a preset to turn it for calibration.
Capacitor (C3):
- Put capacitor C3 in right place just like in the schematic.
Twisted Pair Cable:
- Connect this wire to input and output of the circuit.
Testing and Calibration:
- Use signal generator to send test sound like sine wave.
- Adjust P1 to get clean output with no noise or echo.
Final Steps:
- After testing it fix all wires and parts properly.
- Then connect power supply and turn ON circuit.
Note:
- This is just basic guide one might need extra steps depending on the components used.
- Be safe when working with electronics.
Conclusion:
Simple Full Duplex Audio Line Circuit let two people talk and listen at same time using just one twisted pair wire.
With simple and smart design this circuit makes clear and easy sound communication with no need for big or complicated techniques.
Leave a Reply