Suitable for home audio systems, small PA systems, or individual audio projects, an 18-watt MOSFET audio amplifier is made to drive audio signals with a moderate power output.
This amplifiers usage of MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) has several advantages, including excellent thermal stability, minimal distortion, and high efficiency.
An extensive variety of electrical circuits using the three terminal MOSFET semiconductor transistor.
The oxide insulation separating the conductors allows it to function similarly to a JFET but with less current leakage.
A MOSFET amplifier is any amplifier that uses one of these transistors, they are a suitable alternative for creating linear amplifiers because of their lower load.
Numerous circuits can employ these amplifiers, giving them a broad range of applications.
Circuit Working:
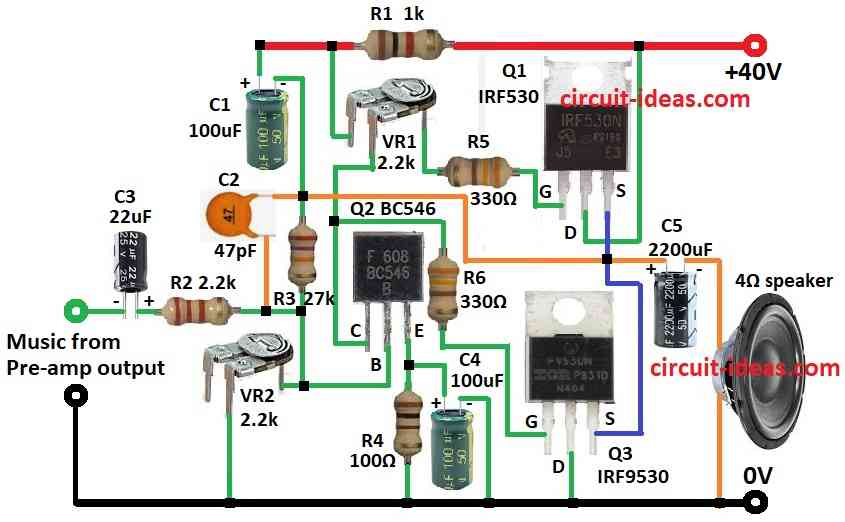
Parts List:
| Component | Value | Quantity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistors | |||
| 1k | 1 | 1/4 watt | |
| 2.2k | 1 | 1/4 watt | |
| 27k | 1 | 1/4 watt | |
| 100Ω | 1 | 1/4 watt | |
| 330Ω | 2 | 1/4 watt | |
| 2.2k | 2 | ||
| Capacitors | |||
| Ceramic Capacitor | 47pF | 1 | |
| Electrolytic Capacitor | 100μF 50V | 2 | |
| 22μF 25V | 1 | ||
| 2200μF 50V | 1 | ||
| Semiconductors | |||
| MOSFET | IRF530 | 1 | |
| MOSFET | IRF9530 | 1 | |
| Transistor | BC546 | 1 | |
| Speaker | 4Ω | 1 |
This circuit is a small sized audio amplifier that is made to produce a lot of power with few parts and excellent sound quality.
With a shunt feedback arrangement, this amplifier uses only one transistor, two MOSFETs and a few resistors and capacitors to produce 18 watts for a 4 ohm speaker.
+40V power supply voltage required to run the amplifier.
Because of the high voltage, the amplifier can efficiently drive a 4 ohm speaker with enough power.
In addition to ensuring constant output power under various loads, a reliable power supply helps minimize noise.
A DC voltage regulator that can provide more than 2 amps at 40V is advised for best results.
An N channel MOSFET IRF530, is used to amplify audio signals.
It is perfect for audio amplification due to its features, which include low on resistance and high input impedance.
Push pull architecture of the IRF9530 P channel MOSFET complements the push pull architecture of the IRF530, enabling consistent and effective output.
As a driver stage, the BC546 NPN Transistor gives the MOSFETs extra gain and makes sure they run within their ideal range.
When component values and circuit design are carefully considered, it can produce strong audio output that is appropriate for a wide range of applications.
Formulas:
A number of important formulas can be used to determine component quantities, power calculations, and overall performance when developing an audio amplifier similar to the one that is discussed.
The following significant equations and ideas may be helpful to built your own amplifier circuit:
Calculating Power Output
You can use the following formula to determine the amplifiers power output into a certain load:
P = Vout2 / Rload
where,
- P is the power output in watts.
- Vout is the RMS root mean square output voltage.
- Rload is the load resistance for 4 ohms
Gain in Voltage
An amplifiers voltage gain can be written as follows:
AV = Vout / Vin
where,
- AV is the voltage gain.
- Vout is the output voltage.
- Vin is the input voltage.
Requirements for Power Supplies:
The power source needs to deliver enough voltage and current for the amplifier to operate at its rated power.
The power supply current for an amplifier is roughly equal to:
Isupply = Poutput / Vsupply
where,
- Isupply is the supply current.
- Poutputt is the output power.
- Vsupply is the supply voltage.
In order to prevent MOSFETs from overheating, their power dissipation needs to be computed:
Pdissipated = (VDS * ID)
where,
- Pdissipated is the power dissipated by the MOSFET.
- VDS is the drain source voltage.
- ID is the drain current.
For the MOSFETs to handle this power dissipation, make sure they are appropriately heatsinked.
Values of Capacitors:
In the circuit, coupling and bypassing are accomplished with capacitors.
The intended cutoff frequency, fc can be used to compute the value of the coupling capacitor C which is C3 and C5 in circuit diagram.
C = 1 / 2πfcR
where,
- C is the capacitance.
- fc is the cutoff frequency.
- R is the resistance in the circuit that the capacitor is coupling with.
Network of Feedback:
The amplifiers gain is set by the feedback resistors.
The closed loop gain CL of a basic shunt feedback amplifier can be found using the following formula:
ACL = 1 + Rf / Ri
where,
- Rf is the feedback resistor R3.
- Ri is the input resistor R2
These formulas and ideas serve as a basis for the construction and analysis of audio amplifiers.
You may estimate performance, find component values, and make sure the amplifier performs within the intended parameters by using these formulas
How to Build:
To build a Simple 18 Watt MOSFET Amplifier Circuit follow the below mentioned steps:
- Gather all the components mentioned in the above circuit diagram.
- Connect collector of transistor Q2 to gate of MOSFET Q3 through resistor R6, and to one leg of preset VR1.
- Connect base of transistor Q2 to first leg of VR2 preset, and second leg of VR2 to ground, connect from base Q2 resistor R3 and capacitor C1 to positive power supply.
- Connect emitter of transistor Q2 to ground through resistor R4, and connect capacitor C4 to ground between emitter of Q2 and resistor R4.
- Connect between base of transistor Q2 and resistor R3 resistor R2 and capacitor C3 in series to music from pre amp output.
- Connect Q1 MOSFET gate from resistor R5 to center leg of VR1 preset, connect drain of MOSFET Q1 to positive supply, connect source of MOSFET Q1 to source of MOSFET Q3.
- Connect MOSFET Q3 gate to collector of transistor Q2, connect drain of MOSFET Q3 to ground, connect source of MOSFET Q3 to source of MOSFET Q1.
- Connect capacitor C2 between resistor R2 and R3 to one end of 4 ohms speaker through capacitor C5 and other end of speaker to ground.
- Connect resistor R1 to positive supply of +40V.
Safety Measures:
You may reduce the dangers involved in working with audio amplifiers and guarantee both circuit dependability and personal safety by following safety precautions.
Your amplifier circuit must be handled, tested, and component managed properly for it to function successfully and safely.
Conclusion:
To conclude, the simple 18 watt MOSFET amplifier circuit design effectively provides significant audio power using a small number of components.
A superior, precisely controlled DC power supply is necessary for maximum performance in order to guarantee stability and minimize noise.
This amplifier offers an affordable option for high quality audio amplification in a variety of applications when components are carefully chosen and safety precautions are followed.
References:
Does a MOSFET amplifier sound different than a standard transistor amp?
Leave a Reply