In this Simple LM386 Audio Amplifier Circuit we use one popular chip called LM386 to make small sound amplifier circuit.
It does not cost much and easy to make and can make speaker or music player sound louder.
It is not very powerful for big show but good for small projects.
And also is good way to learn electronics and make music sound better.
What is a LM386 Audio Amplifier:
LM386 is very common chip used for making low power audio amplifier.
People use it in small audio things like portable speaker, intercom and DIY projects because it easy to use, cheap and simple.
It help to make sound louder in small electronics projects.
Understanding LM386:
LM386 is old but still useful audio amplifier chip with class AB type. People still use it in small speakers and portable stereo.
Like in pin diagram LM386 comes in common 8-pin DIP package.
Pin Functions and Gain Control:

When we see the pin diagram design is simple with only few wires needed.
Normal gain is 20 and it works like that with pin 1 and pin 8.
If we put capacitor between pin 1 and 8 gain goes up to 200 because it skip the inside resistor.
Op-amp inside chip uses pin 2 and 3. Pin 2 is for inverting pin 3 is for non-inverting input.
Audio input come from mic, laptop, music player or phone and connect to input pin.
Power Supply and Output:
Pin 6 and pin 4 are for power and this chip can take up to 15V.
In this project we have used 12V power.
Pin 7 help with decoupling but we need to put capacitor to connect ground there.
Output comes from pin 5 and before connecting to speaker we must control it properly to stop any damage from DC signal.
Applications of LM386:
LM386 chip is used a lot in audio world an is the main part in small speakers, music players, laptop speaker, TV sound, FM radio, mic voice recorder and battery speakers.
Because it can work in many ways as it is popular in many audio projects.
Circuit Working:
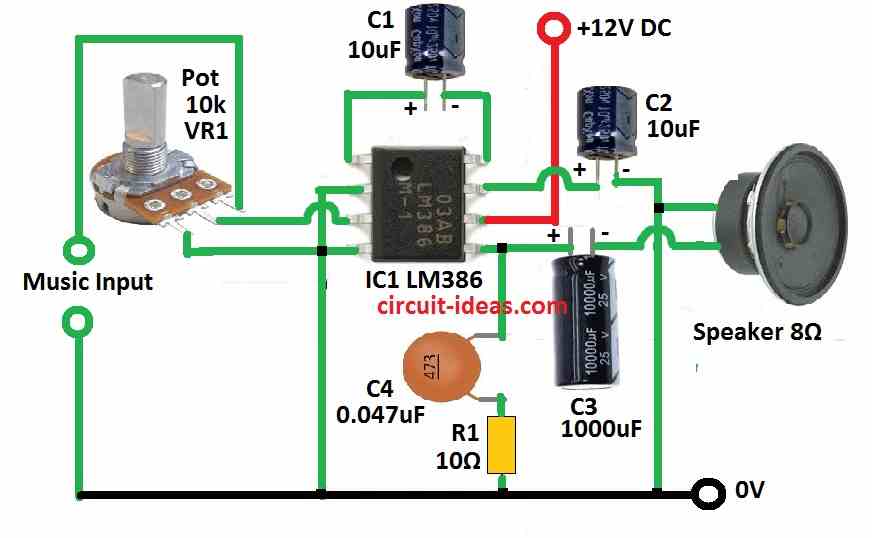
Parts List:
| Category | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 10Ω 1/4 W CFR | 1 |
| Potentiometer 10k | 1 | |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 0.047µF | 1 |
| Electrolytic 10µF 25V | 2 | |
| Electrolytic 1000µF 25V | 1 | |
| Semiconductor | IC LM386 | 1 |
| Speaker 8Ω | 1 |
LM386 Audio Amplifier Circuit:
This circuit makes small audio signal louder so it can power a speaker.
LM386 works with low voltage power between 4V to 15V.
In this project we have used 12V power supply.
To give power to the chip we have connected pin 6 (V+) to positive and pin 4 (V−) to ground.
Gain Control:
Pin 1 and pin 8 control the gain which is loudness boost.
Normally gain is set to 20.
If we put a capacitor between pin 1 and 8 we can skip the chips inside resistor and make gain go up to 200.
In this circuit we have used a 10μF capacitor for that.
Audio Input:
Audio goes into pin 2 and pin 3.
Pin 2 (inverting input) is connected to ground.
Pin 3 (non-inverting input) connects to tip of 3.5mm audio jack like from phone or laptop.
The sleeve outer part of the jack connects to ground.
Output Stage:
Pin 5 is output.
We connect a 0.047μF capacitor to pin 5 and this capacitor blocks DC and only lets audio signal AC go to speaker.
Other side of this capacitor connects to positive power.
Pin 5 also goes to speakers positive side.
Speakers negative side is connected to ground.
This setup lets speaker play the loud sound from the amplifier.
Bypass Capacitor:
Pin 7 is bypass pin.
We have put 250μF capacitor here.
This capacitor helps remove noise from power and keeps the chip working stable.
Formulas with Calculations:
Formulas and Calculations for Simple LM386 Audio Amplifier:
1. Output Capacitor Cut-off Frequency (High-pass Filter):
We use this to find low frequency limit for audio signal going to speaker.
Formula:
fc = 1 / (2 × π × Rload × C3)
where:
- fc is cut-off frequency in Hz
- Rload is speaker resistance to 8 ohms
- C3 is output capacitor = 1000µF = 1000 × 10⁻⁶ farads
Calculation:
fc = 1 / (2 × π × 8 × 1000 × 10⁻⁶)
fc = 19.89 Hz
So low sound below 19.89 Hz will be blocked.
2. Zobel Network Cut-off Frequency for Stability:
Zobel network helps to keep amplifier stable and reduce noise at high frequency.
Formula:
fz = 1 / (2 × π × R1 × C4)
where:
- fz is cut-off frequency in Hz
- R1 is resistor = 10Ω
- C4 is capacitor = 0.047µF = 0.047 × 10⁻⁶ farads
Calculation:
fz = 1 / (2 × π × 10 × 0.047 × 10⁻⁶)
fz = 338600 Hz or 338.6 kHz
So very high frequency above 338.6 kHz gets filtered.
How to Build:
To build a Simple LM386 Audio Amplifier Circuit follow the steps mentioned below:
LM386 Pin Connections:
- Put LM386 chip on the PCB board.
- Connect pin 4 to ground.
- Connect pin 6 to +12V power supply.
Gain Control:
- Connect pin 1 and pin 8 using 10k resistor.
- To make gain of 20 put 10μF capacitor between pin 1 and 8.
- If we want to change gain easily then use a potentiometer between pin 1 and 8.
Audio Input:
- Connect pin 2 to ground.
- Connect pin 3 to tip of 3.5mm audio jack.
- Connect audio jack sleeve to ground.
Power Supply:
- Pin 6 connects to positive 12V,
- Pin 4 connects to ground.
Output Stage:
- Connect pin 5 to a 0.047μF ceramic capacitor.
- Other side of this capacitor connects to positive power.
- Also connect pin 5 to positive terminal of speaker.
- Connect speaker negative terminal to ground.
Bypass Capacitor:
- Connect pin 7 to a 250μF capacitor,
- Other side of capacitor connects to ground.
- This helps remove noise from power.
Conclusion:
If we follow these steps then we can build a Simple LM386 Audio Amplifier Circuit that works well.
We can test with different parts and change values to make sound better for our own needs.
Leave a Reply