To get good sound with less power and work for long time is very important in audio amplifier.
This 50 Watts Audio Amplifier Circuit give strong sound and work well.
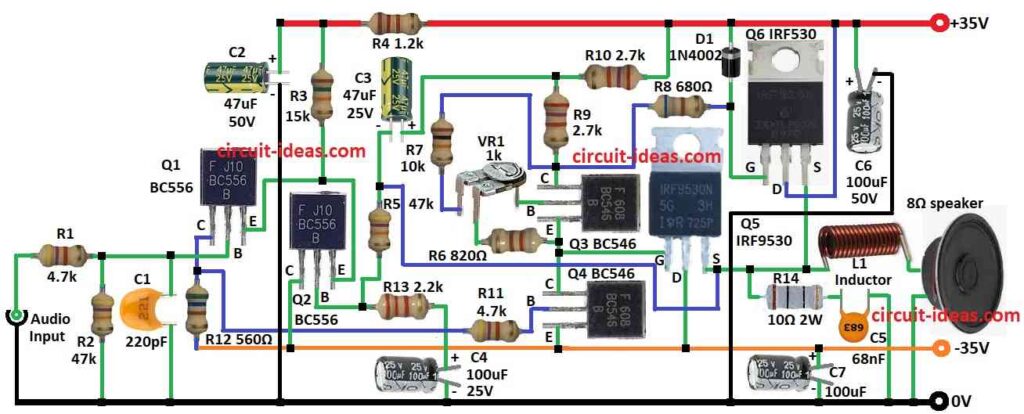
It uses both MOSFET and BJT to make clear sound and can run 8 ohm speaker with full 50 watt power.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Component Type | Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors (All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified) | 15k | 1 |
| 1.2k | 1 | |
| 680Ω | 1 | |
| 560Ω | 1 | |
| 820Ω | 1 | |
| 10k | 1 | |
| 2.2k | 1 | |
| 10Ω 2W | 1 | |
| 47k | 2 | |
| 2.7k | 2 | |
| 4.7k | 2 | |
| Preset 1k | 1 | |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 220pF | 1 |
| Ceramic 68nF | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 47μF 50V C2 | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 47μF 25V | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 100μF 50V C6 | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 100μF 25V | 2 | |
| Semiconductors | MOSFET IRF530 | 1 |
| MOSFET IRF9530 | 1 | |
| Transistor BC556 | 2 | |
| Transistor BC546 | 2 | |
| Diode 1N4002 | 1 | |
| Inductor Coil (12 turns of enameled copper wire on a 1cm diameter plastic former) | 1 | |
| Speaker 8Ω | 1 |
This 50 watt audio amplifier gives strong sound with low distortion.
Q1 and Q2 transistors work as differential amplifier to start the circuit.
R1 controls input current and C1 removes high frequency noise and blocks DC from input.
Next step is driver stage with Q3 and Q4 transistors.
Output stage uses IRF530 and IRF9530 MOSFETs in push-pull setup.
L1 coil connects output to speaker.
R14 and C5 help reduce noise and C6 and C7 clean the power supply.
VR1 sets the idle (quiescent) current.
Build circuit on good PCB and use +/-35V dual power supply.
For L1 wind 12 turns of copper wire enameled on 1 cm plastic tube.
All other electrolytic capacitors can be 10V or 15V but C6 and C7 must be 50V.
MOSFETs need heat sink with bigger is better.
A 8x4x4 inch aluminum finned heat sink is good.
Formulas:
Formulas for 50W Audio Amplifier Circuit:
1. Differential Amplifier Stage:
Uses Q1 and Q2 transistors.
C1 is input DC blocker (decoupler).
Choose C1 based on cutoff frequency and input resistance.
Formula:
fc = 1 / (2π × Rin × C1)
where,
- Rin is the input resistance
- C1 is the input capacitor
2. Output Stage:
Uses IRF530 N-channel and IRF9530 P-channel in push-pull design.
Output goes to speaker through inductor L1.
L1 filters high frequency noise.
Formula for L1:
L1 = 1 / (2π × fcutoff × Cspeaker)
where,
- Cspeaker is the capacitance of speaker which is usually small
3. Noise Filter Network:
R14 and C5 reduce noise together.
Formula:
fnoise = 1 / (2π × R14 × C5)
4. L1 Inductor Design:
Wind 12 turns copper wire on 1 cm plastic tube.
Formula for L1 inductance:
L = (μ0 × μr × N² × A) / l
where:
- μ0 is the permeability of air
- μr is the relative permeability
- N is the number of turns
- A is the coil area
- l is the length of coil
How to Build:
To build a 50 Watts Audio Amplifier Circuit follow the below mentioned steps:
- Q1 get input audio on base goes to ground through R1 and C1.
- Q1 and Q2 share same emitter.
- Q1 collector goes to -35V through R12 and to Q4 base via R11.
- Q2 collector goes direct to -35V.
- Q2 base goes to ground via R13 and C4 and also connect to R5, C3 and R10 to +35V.
- Q3 base goes to middle leg of preset VR1 emitter go to second leg of VR1 through R6, collector to R9.
- Q4 base connect to Q1 collector, emitter to -35V and collector to Q3 emitter.
- Q5 gate connect to Q3, emitter drain to -35V and source to L1 and Q6 source.
- L1 goes to one side of speaker and other side to ground.
- R14 and C5 connect from Q5 source to ground noise filter.
- C7 connect from -35V to ground power filter.
- Q6 gate connect to +35V through D1 and also R7 and R8 from VR1 third leg.
- Q6 drain goes to +35V and source join Q5 source.
- C2 and C6 clean power filter capacitors.
Conclusion:
This 50 Watts Audio Amplifier Circuit uses good parts and strong layout.
Sound come out loud and clear.
Work good for home and pro audio both.
Circuit give steady and clean sound all time.