Controlling the direction a DC motor spins can be done easily with a circuit that uses the IC 555 Timer.
This method is really useful in areas like automation, robotics and other motorized gadgets where you need to switch between moving forward and backward.
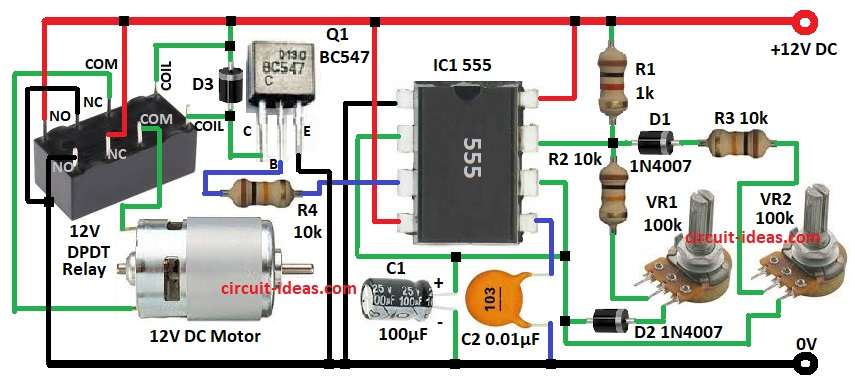
The circuit includes a 555 timer chip, a transistor and a DPDT relay all working together to change the motors direction.
This design is not only simple but also easy to put together making it a great option for driving a DC motor in both directions.
The circuit works by using the output from an astable multivibrator, which is based on the IC 555 timer to control the relay that powers the motor.
You can easily power the circuit with a 12V DC power supply making it simple to use in different systems.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Component | Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 1k, 1/4 watt | 1 |
| 10k | 3 | |
| Potentiometer | 100k | 2 |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 0.01µF | 1 |
| Electrolytic 100µF 25V | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | IC Timer 555 | 1 |
| Transistor BC547 | 1 | |
| Diode 1N4007 | 3 | |
| Other Components | 12V DPDT Relay | 1 |
| 12V DC Motor | 1 |
The circuit here is cleverly designed using the 555 timer integrated circuit, which acts as a astable mutivibrator.
This means it helps control a relay that manages the direction of a motor.
The 555 timer is in astable mutivibrator mode which means it can create a pulse output.
The trigger pin known as pin 2 connects to a voltage divider made of resistors R3 and VR2 along with capacitor C1.
When the circuit is turned on the output at pin 3 goes high for a time determined by the resistor and capacitor combination.
Transistor Q1 acts like a switch that powers the relay coil.
It works based on the signal from the 555 timer IC.
When the timers output is high the transistor turns on allowing current to flow through the relay coil.
The relay is important because it changes the polarity of the motor connections.
When it is not powered, it connects the motor to one polarity.
When it is powered it flips the polarity making the motor spin in the opposite direction.
Diodes D1 and D2 are used to protect the timer circuit from reverse voltage.
Diodes D3 act as freewheeling diode which protect both the relay and the transistor from voltage spikes.
The direction the motor spins depends on how the relay is switched, allowing for different operations based on the relays setup.
Formulas with Calculations:
Below mentioned are the formulas with calculations for Controlling a DC Motors Direction Circuit with IC 555 Timer:
Astable Multivibrator Frequency:
The frequency of oscillation for an astable multivibrator using the 555 timer is given by:
Frequency (f) = 1.44 / ((R3 + 2VR2 × C1)
where,
- R3 is 10k resistor in the circuit diagram
- VR2 is 100kΩ potentiometer in the circuit diagram
- C1 is 100µF capacitor in the circuit diagram
Substituting these values:
f = 1.44 / ((10K + 2 × 100K) × 100µF)
f = 1.44 / ((10,000 + 200,000) × 0.0001)
f = 1.44 / (210,000 × 0.0001)
f = 1.44 / 21
f = 0.0685 Hz
This means the ON/OFF switching happens every:
Time Period (T) = 1 / f = 1 / 0.0685 = 14.6 seconds
So, the motor switches direction approximately every 14.6 seconds.
How to Build:
For Controlling a DC Motors Direction Circuit with IC 555 Timer follow the below mentioned steps for connections of your own circuit for better understanding:
- Gather all the components mentioned in the above circuit diagram
- Connect pin 1 of IC1 to GND of the circuit
- Connect pin 2 of IC1 to pin 6 of IC1.
- Connect pin 3 of IC1 to base of transistor Q1 through resistor R4
- Connect pin 4 and pin 8 of IC1 to +12V DC power supply
- Connect pin 5 of IC1 to GND through capacitor C2
- Connect pin 7 of IC1 between resistor R1 and R2
- Connect pot VR1 one end connect to resistor R2 and other end connect to cathode of diode D2 and connect the anode of D2 to pin 2 of IC1
- Connect the anode of diode D1 from pin 7 of IC1 cathode of D1 diode connect to one end of resistor R3 and other end of R3 connect to one end of pot VR2 and other end of VR2 pot connect to anode of diode D2
- Connect positive of capacitor C1 to pin 2 of IC1 and negative of C1 connect to GND.
- Connect collector of transistor Q1 to positive supply through diode D3
- Connect emitter of transistor Q1 to GND
- Connect the other COIL pin of 12V relay to cathode of diode D3
- Connect the Common poles of DPDT relay to the 12V motor terminals
- Connect the one NC contact of the DPDT relay with the positive supply and the other NC contact connect to negative supply
- Connect the one NO contact of the DPDT relay with the positive supply and the other NO contact connect to negative supply
Conclusion:
This Controlling a DC Motors Direction Circuit with IC 555 Timer can change the direction of a DC motor easily and effectively.
It uses a relay and a 555 timer IC, which makes it great for things like automation, conveyor belts and robots that need to move back and forth.
The relay helps keep the circuit safe by providing electrical isolation, so you can trust that it will work reliably.
Leave a Reply