This easy and Simple Entrance Alarm Circuit is made to protect door or way where people enter.
It makes loud sound when someone walk through invisible IR light.
It works good at day and night by not giving much wrong alarm.
The circuit is simple and good for hobby people during nighttime.
Circuit Working:
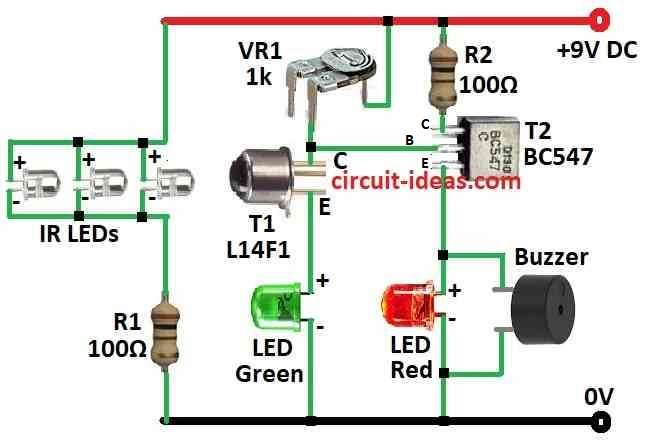
Parts List:
| Category | Item | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 100Ω 1/4 watt | 2 |
| Preset 1k | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | Photo transistor L14F1 or similar type | 1 |
| Transistor BC547 | 1 | |
| LED Green 5mm 20mA | 1 | |
| LED Red 5mm 20mA | 1 | |
| IR transmitter LEDs | 3 | |
| Buzzer | 1 |
This circuit use IR diodes to send out infrared light all time but not like remote that send in short pulses.
It uses one NPN darlington phototransistor to see the light.
The L14F1 is very sensitive phototransistor with big gain.
Its collector connects to positive side through VR1 and emitter have green LED to show standby.
Base of T1 is not connected as the light comes through T1 window to hit base and make it work.
When there is more light more it works.
T2 work as driver for alarm and its base connect to T1s collector so it depends on T1 working.
When IR light fall on phototransistor it works and pull T1 base to ground and T1 stay OFF
In this case the red LED and buzzer ON T2 emitter as it stays OFF
When someone break the IR beam the T1 stops working and so its collector voltage goes up.
Then T2 turns ON and red LED + buzzer also turn ON.
We can build this circuit on small PCB board.
Put R1 and IR LEDs on different small board and keep IR LEDs on one side of door and phototransistor on other side.
Point IR light properly to phototransistor so buzzer stays quiet when no one passes.
Wave hand in middle to test and check buzzer should make sound.
Use VR1 to adjust T2 base bias, so buzzer stays OFF when no one is around.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Entrance Alarm Circuit we need to follow the below mentioned steps:
Make IR LED Board:
- Put IR LEDs and one resistor R1 on different small board.
- Resistor value depend on which IR LED we will use.
- This board will send invisible IR light.
Make Phototransistor Board:
- Fix phototransistor L14F1 on other board.
- Ensure IR light from LED board connects straight to this phototransistor.
Build Main Circuit:
- Put phototransistor L14F1 on main PCB board.
- Connect its collector to positive side with VR1 preset.
- Connect emitter to ground.
Connect LEDs and Buzzer:
- Green LED connects to emitter of phototransistor which will show standby mode.
- Red LED and buzzer connects to emitter of another NPN transistor T2 for alarm.
Connect T2 Base:
- Connect base of T2 to collector of phototransistor T1.
- This will decide when alarm will turn ON.
Give Power:
- Connect battery or power to circuit and be careful with plus and minus.
Adjust VR1:
- Use VR1 to set T2 base level and buzzer should stay OFF when no one passes.
Test the Circuit:
- Wave hand in front of IR beam.
- If circuit work then buzzer will make sound.
Mount Everything:
- Put full circuit in good box.
- Be sure IR LED board and phototransistor board face each other.
- Line up beam properly.
Finish:
- Tie all the wires and parts and check they are safe now we can see IR beam alarm is ready to use!
Note:
- Be careful and always remove power before changing wires.
- Check all parts are connected tight.
Conclusion:
To conclude this Simple Entrance Alarm Circuit is easy and useful way to protect door or entrance.
It work good in day and night and does not gives any wrong alarms.
Because circuit is simple it is very good small project for hobby people who like home security ideas.