Building an LDR Comparator Circuit using IC LM339 is useful and important in many electronic jobs like sensing and control.
Using LDR, resistors, LED and LM339 IC we can make a simple circuit to check light level and show light change.
LDR works like light sensor and its resistance changes when light changes.
Using preset and fixed resistor we can make voltage divider and this voltage changes when light changes.
IC LM339 compares this voltage with a fixed reference voltage from resistor.
If light goes above set level then comparator sends signal and LED turns ON to show light change.
This circuit shows voltage compare, sensing and output signal which is easy to build and is good for learning.
It is used in small light based tools or big systems.
IC LM339 with LDR is great example of simple parts doing useful work.
Circuit Working:
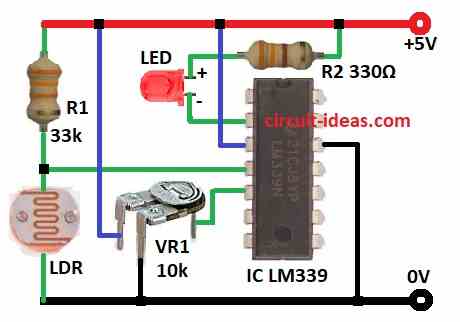
Parts List:
| Component | Value | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 33k 1/4 watt | 1 |
| 330Ω 1/4 watt | 1 | |
| Preset 10k | 1 | |
| LDR | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | IC LM339 | 1 |
| LED 5mm 20mA | 1 |
IC LM339 is quad comparator.
Only one comparator is used in this LDR circuit.
LDR is light sensor and its resistance changes with light.
More light means less resistance.
Resistor R1 makes voltage divider and LDR connects to pin 4.
When light increases the LDR resistance drops and voltage at pin 4 goes up and pin 3 gives low output.
Pin 5 has variable resistor VR1.
If VR1 is low then voltage at pin 5 goes high.
To get good output in low light then pin 4 inverting input must stay below pin 5 voltage.
When LDR sees more light then resistance drops and output voltage increases.
Comparator changes output when pin 4 inverting voltage crosses pin 5 non-inverting voltage.
In dark the LDR resistance is high and LED turns ON.
Formulas:
Main formulas for LDR comparator circuit using LM339:
1. Voltage Divider for pin 4 inverting input:
Vpin4 = (RLDR / (RLDR + R1)) × VCC
where,
- Vpin4 is the voltage at pin 4
- RLDR is the LDR resistance which changes with light
- R1 is the fixed resistor with 33k
- VCC is the 5V supply
2. Voltage at pin 5 for non-inverting input:
Vpin5 = (R2 / (R1 + R2)) × VCC
where,
- R2 is the VR1 for variable resistor setting
- VCC is the 5V supply
3. LED Current:
ILED = (VCC − VLED) / R2
where,
- VLED is the LED forward voltage to about 2V
- R2 is the resistor to limit current for 330Ω
These formulas help to set correct voltage and current in the circuit.
We can adjust VR1 to change how sensitive the circuit is to light.
How to Build:
For Building an LDR Comparator Circuit using IC LM339 follow the below mentioned steps for connections:
- Connect pin 2 of LM339 to +5V through LED and 330Ω R2 resistor.
- Connect pin 3 to +5V.
- Connect pin 4 to the point where R1 33k and LDR join.
- Other end of LDR goes to GND.
- Connect pin 5 to middle pin of VR1.
- One side of VR1 goes to +5V and other side to GND.
- Connect pin 12 of LM339 to GND.
Conclusion:
Building an LDR Comparator Circuit using IC LM339 shows how to compare voltage and detect light.
It checks light level using LDR and preset resistor and gives output like LED ON/OFF.
Circuit can be changed easily to use in other projects like relay or buzzer too.
It is good for learning basics and is useful for bigger sensing circuits later.
References:
Photocell comparator circuit using LM339