Regular car batteries have a liquid inside, but gel cell batteries are like a special type that uses a jelly instead.
This jelly makes them tougher and lets you use them in different positions.
To charge these gel cell batteries safely, you need a special charger circuit.
This charger is like a smart helper that fills the battery with just the right amount of power,
without going overboard.
Overfilling can damage the battery, so this special charger keeps it healthy and happy.
Circuit Working:
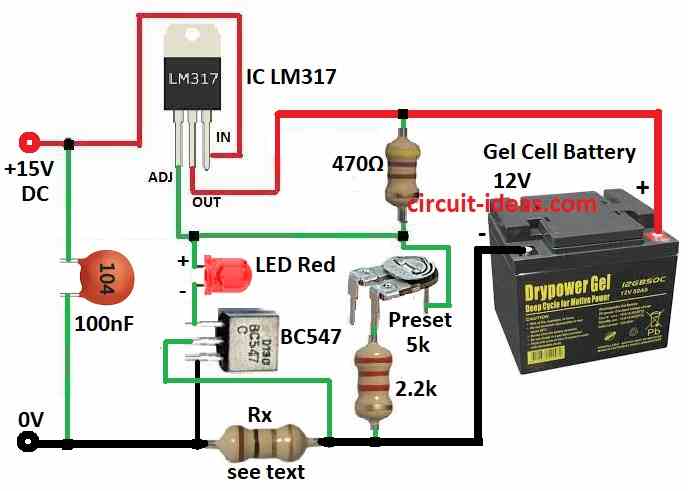
Parts List:
| Category | Item | Quantity | Additional Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 470Ω, 2.2k | 1 each | All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified |
| Rx | 1 | Rx = 0.7/max current | |
| Preset 5k | 1 | ||
| Capacitor | Ceramic 100nF | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | IC LM317 | 1 | |
| Transistor BC547 | 1 | ||
| LED Red 5mm 20mA | 1 | ||
| Battery | 12V Gel cell battery | 1 |
This circuit can charge gel cell batteries at 300mA, 650mA or 1.3A depending on the current sensing resistor in the 0V supply.
To set the output voltage to 13.4V adjust the 5k preset .
When the battery voltage reaches this level the current will decrease to a few milliamps.
Upgrading the plug pack is necessary for the 650mA or 1.3A charge current.
The red LED indicates charging and as the battery voltage increases the current flow decreases.
The maximum current is indicated below and when it decreases by about 5%, the LED turns off and the current gradually decreases to almost zero.
Formulas:
The following formula may be used to get the output voltage Vout of a circuit using two external resistors in an LM317 voltage regulator:
Vout = 1.25V * (1 + R2 / R1)
where,
- Vout is the desired output voltage, expressed in volts.
- 1.25V is the constant internal reference voltage of the LM317.
- R2 is the resistors value (here in diagram preset + 2.2k ) that is attached to the adjust and output pins.
- R1 is the resistors value (here in diagram 470 ohms) between the adjust pin and ground
Take note:
The LM317s adjust pin (Iadj) normally has very little current flowing through it (about 50 microamps), therefore most applications can ignore it.
For this reason, the formula does not incorporate it.
Use resistors with 1% tolerance or greater for optimal precision.
Here are a few more things to think about:
Since the LM317 has an internal reference voltage, its minimum output voltage is around 1.25V.
The input voltage and the LM317s dropout voltage, which is normally between two and three volts, limit the maximum output voltage.
To calculate the values of R1 and R2 for a desired output voltage, you can use internet calculators.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Gel Cell Battery Charger Circuit follow the below mentioned steps for connections:
Design the Circuit:
Select appropriate components as shown in diagram
Build the Power Supply Section:
- Connect the input pint of IC LM317 to +15V DC charging input..
- Connect the out pin of IC LM317 to 12V gel cell battery through a 470 ohm resistor.
- Connect the adj pin of IC LM317 through a red LED and a transistor BC547.
Build the Voltage Regulator Section:
- Use a voltage regulator IC such as LM317 to regulate the charging voltage.
- Use resistors and a preset to set the output voltage to the desired level .
Build the Current Limiting Section:
- Use a current sensing resistor in the 0V supply to set the charging current.
- Include transistors and resistors for current control.
Add Indicator Lights:
- Use LED to indicate charging status.
- Connect the LED to the circuit to show when the battery is charging and when it is fully charged.
Test the Circuit:
- Before connecting the gel cell battery test the circuit with a dummy load to ensure it is working correctly.
- Once the circuit is confirmed to be working connect it to the gel cell battery for charging.
Monitor the Charging Process:
- Monitor the voltage and current during the charging process to ensure they are within the specified limits.
- Disconnect the charger once the battery is fully charged.
Safety Precautions:
- Use appropriate safety measures to prevent short circuits and overheating.
- Follow the manufacturers guidelines for charging the gel cell battery.
Note:
- Please note that building a battery charger involves working with potentially dangerous voltages.
- If you are not experienced with electronics or are unsure about any aspect of the circuit seek assistance from someone with expertise in electronics.
Conclusion:
A gel cell battery charger circuit is designed to safely and efficiently charge gel cell batteries.
It typically includes a transformer, rectifier, voltage regulator and current limiting circuitry.
The circuit ensures that the battery is charged to its full capacity without overcharging which can damage the battery.
Leave a Reply