This Simple Voltage Regulator Circuit using Transistor and Zener work like bodyguard for electricity.
It uses one transistor like door keeper and one special Zener diode to keep voltage not going up-down.
Zener diode gives fixed voltage and transistor follow that voltage to keep same for our device.
This project is good when voltage goes crazy and makes problem.
Also transistor can take big power so it is good if our project which need big electric push.
What is a Voltage Regulator Circuit using Transistor and Zener:
A easy way to control and fix power supply voltage is using one transistor and one Zener diode in voltage regulator circuit.
This type of circuit are used many time in power supply and electronic stuff where steady voltage is needed.
Circuit Working:
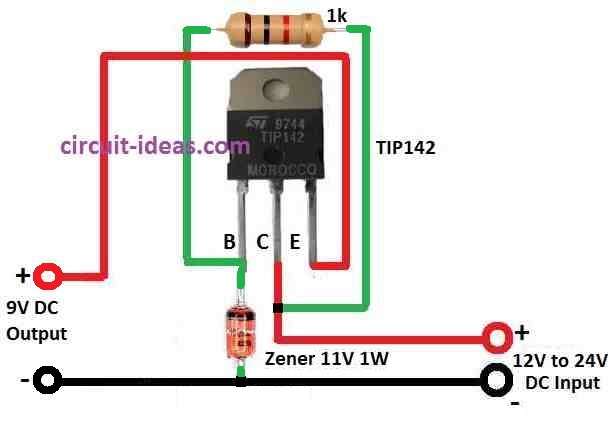
Parts List:
| Type | Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 1k | 1 |
| Semiconductors | Transistor TIP142 | 1 |
| Zener 11V 1W | 1 |
This one is Darlington NPN power transistor.
It is having two NPN transistors which join together in Darlington way so it gives big current gain.
Zener diode uses this like a voltage reference.
When voltage reaches Zener level it starts working backward and keep voltage almost same.
One resistor is put with TIP142 base to stop too much current going inside the base.
Circuit Operation:
When voltage on Zener diode reaches Zener level it starts working backward (reverse) and start to conduct.
We have given 11V DC to power this circuit.
Zener diode connects to base of TIP142.
With this base of transistor get steady 11V.
TIP142 work like emitter follower and emitter copy base voltage but little less to around 2V less because of Darlington setup.
So this setup gives stable voltage output.
Because Zener keep base at 11V the emitter gives around 11V minus 2V that is near to 9V.
So we get fixed 9V output between emitter and ground.
Darlington type make voltage drop near 2V and we count this drop when we find output voltage.
Formulas:
Here are some easy formula to control DC input voltage to fixed output voltage.
Base Resistor (Rb):
Base resistor (Rb) controls how much current goes in transistor and gives proper bias which uses this formula:
Rb = (Vin – Vz) / Ib
where:
- Vin is input voltage like 12V to 24V
- Vz is Zener diode voltage like 11V
- Ib is base current which is around 1mA
Power Loss in Resistor (Rb):
Resistor (Rb) stop too much current from going in base so it loses some energy for that below formula is used:
Prb = (Vin – Vz)² / Rb
where:
- Prb is power loss in resistor Rb
Remember:
Transistor base emitter voltage (Vbe) is about 0.7V.
To make transistor work properly in active zone, Zener diode must get enough current not too much or too low.
Choose right value of Rb and for this check TIP142 datasheet.
It tells about transistor gain (β) which help to find better Rb value.
How to Build:
To Build a Simple Voltage Regulator Circuit using Transistor and Zener below mentioned are the connections steps:
- TIP142 collector connects to positive supply (Vcc).
- Emitter of TIP142 connects to load resistor and then to ground.
- Base of TIP142 connect to anode of Zener diode.
- Cathode of Zener diode connects to ground.
- Base also connect to one resistor in series.
- Value of this resistor is found using ohms law.
- Load resistor connects between emitter of TIP142 and ground (This is our device or circuit we want to power.)
- Power supply connect to TIP142 collector.
Testing:
- Connect power supply.
- Use multimeter to check voltage across load resistor.
- It should show around 9V and this is regulated output.
- If we need different output voltage then change value of base resistor.
Notes:
- Always check TIP142 and Zener diode datasheets for ratings.
- Do not give too high voltage it may break parts.
- If using big power give TIP142 proper heat sink to stay cool.
Conclusion:
In this Simple Voltage Regulator Circuit using Transistor and Zener at TIP142 base Zener diode give steady voltage like reference.
Transistor works like emitter follower so output voltage stay near 9V and does not change too much.
Darlington type have big current gain so it is good for circuits that need more current.