Resistors can help in some ways but they are not good for smoothly changing motor speed.
That is why a smart PWM Motor Speed Control Circuit using Two Transistors is used.
It works like a dimmer switch for the motor.
We turn a knob like a potentiometer to change how much power the transistors get.
This controls the motor speed.
Circuit Working:
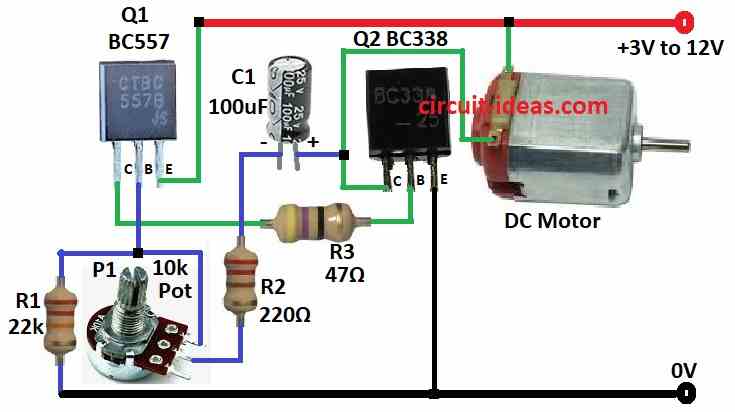
Parts List:
| Component Type | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors (All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified) | 22k | 1 |
| 220Ω | 1 | |
| 47Ω | 1 | |
| Potentiometer 10k | 1 | |
| Capacitors | Electrolytic 100µF 25V | 1 |
| Semiconductors | Transistor BC557 | 1 |
| Transistor BC338 | 1 | |
| DC Motor | 1 |
This is a simple motor speed controller using two transistors.
It is better than using a resistor for two main reasons:
Resistors waste energy as heat but this circuit sends most of the power directly to the motor.
Resistors can make the motor start roughly while this circuit runs it smoothly.
The circuit uses PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to control speed.
It turns the motor ON and OFF very quickly.
The longer it is ON higher duty cycle and the faster the motor runs.
The shorter it is ON lower the duty cycle and slower it goes.
This fast switching makes the motor run smoothly.
How the circuit works:
It uses two transistors one PNP BC557 and one NPN BC338.
They are set up in a Darlington pair to boost current and letting it handle bigger motors.
A potentiometer controls the motor speed.
Turning the knob changes the voltage at the NPN transistors base.
This controls how much current flows through the motor and by adjusting its speed.
Formulas:
This circuit controls the DC motor speed using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation).
Duty Cycle Formula:
The duty cycle D tells how long the signal stays ON and is calculated as:
D = (Rpot / (Rpot + Rfixed)) × 100%
- Rpot is the variable resistance from the potentiometer from 0 to 10kΩ.
- Rfixed is the value of the fixed resistor in the circuit.
Motor Speed Control:
The motor speed depends on the average voltage from the PWM signal.
A higher duty cycle means more voltage and faster speed.
A lower duty cycle means less voltage and slower speed.
Important Notes:
Use the correct transistors like BC338 to control motor current and BC557 to generate the PWM signal.
We can add a capacitor to smooth out the PWM signal.
Choose resistor values that match the transistors current gain β so they get enough base current.
This circuit works using just transistors and a few basic parts.
How to Build:
To build a PWM Motor Speed Control Circuit follow the below mentioned steps for assembling:
- Join Q1s collector to Q2s base using resistor R3.
- Connect Q1s base between resistor R1 and P1 potentiometer.
- Link Q1s emitter to the positive (+) power supply.
- Connect Q2s collector to one wire of the DC motor.
- Join Q2s base to Q1s collector.
- Connect Q2s emitter to ground (-).
- Connect one side of capacitor C1 to Q2s collector and the other side to the potentiometer through resistor R2.
- Connect other wire of the DC motor to the positive (+) power supply.
Note:
- Want more features? Like reverse motor or protect from overload then use motor driver ICs.
- Be careful and handle electrical parts safely.
Conclusion:
Using resistors to slow down motor is easy but it wastes power and makes motor run rough.
Using two transistors is better and it saves power.
With potentiometer we can change motor speed slowly and smoothly.
This PWM Motor Speed Control Circuit using Two Transistors is a good and easy choice for simple motor speed control.
Leave a Reply