Resistors are helpful for many things, but they are not the best choice for changing motor speed smoothly.
That is where a clever circuit with just two transistors comes in.
This circuit acts like a fancy dimmer switch for your motor.
By turning a knob called a potentiometer, you control the power going to the transistors.
This, in turn controls how fast the motor spins.
Circuit Working:
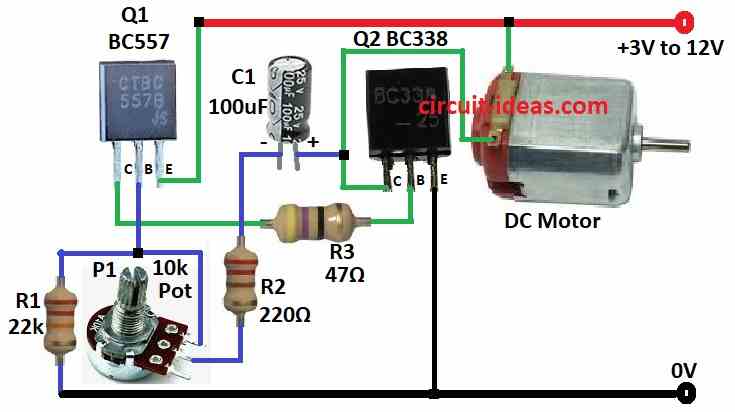
Parts List:
| Component Type | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors (All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified) | 22k | 1 |
| 220Ω | 1 | |
| 47Ω | 1 | |
| Potentiometer | 10k | 1 |
| Capacitors | Electrolytic 100µF 25V | 1 |
| Semiconductors | Transistor BC557 | 1 |
| Transistor BC338 | 1 | |
| Other | DC Motor | 1 |
This is a simple motor speed controller circuit that uses two transistors.
It is indeed better than reducing the RPM of a motor via a resistor in two ways:
When you use a resistor to control the speed of a motor, the resistor dissipates the excess power as heat.
This is wasted energy.
In the transistor circuit the transistors act as switches allowing almost all of the power to go to the motor.
The resistor method reduces the voltage supplied to the motor, which can cause it to jerk or hesitate when starting.
The transistor circuit uses pulse width modulation PWM to control the motor speed.
PWM rapidly switches the motor on and off.
The average amount of time the motor is on compared to the time it is off controls the speed.
A higher duty cycle more on time means the motor spins faster and a lower duty cycle more off time means the motor spins slower.
This on-off switching happens very quickly so the motor appears to run smoothly.
Below is circuit working process:
- The circuit uses two transistors, one PNP BC557 and one NPN(BC338.
- The transistors are connected in a darlington pair configuration which increases the current gain of the circuit.
- This allows the circuit to control a larger motor than a single transistor could handle.
- The speed control is achieved using a potentiometer P1.
- As you rotate the knob of the potentiometer, you change the voltage at the base of the NPN transistor BC338.
- The voltage at the base of the NPN transistor controls how much current flows through it which in turn controls how much current flows through the motor.
Formulas:
To regulate the speed of the DC motor, the circuit uses the PWM concept.
Here is a basic formula to help you comprehend how it works:
Duty Cycle Calculation:
The duty cycle D is computed as follows:
D = Rpot / Rpot +Rfixed×100%
where,
- Rpot is the resistance that is determined by the potentiometer, which has a range of 0 to 10k
- The circuits fixed resistor value is denoted by Rfixed.
Motor Speed Control:
Because the PWM signals duty cycle controls the average voltage delivered, the motor speed Vmotor is directly proportional to that voltage.
Note:
Make sure you choose the right transistors (BC338 for motor current regulation and BC557 for PWM signal generating).
If necessary, the capacitor can be utilized to smooth the PWM signal by filtering it.
It is important to select resistor values that respect the transistors current gain (β) and guarantee the transistors get the correct base current.
Using transistors and other basic components, this simple circuit offers a framework for PWM motor speed control that is appropriate for low power DC motors operating within the given voltage range.
How to Build:
To build a PWM Motor Speed Control Circuit follow the below mentioned steps for assembling:
- Connect collector of transistor Q1 to base of Q2 through R3 resistor.
- Connect base of transistor Q1 between R1 resistor and P1 pot.
- Connect emitter of transistor Q1 to positive power supply.
- Connect collector of transistor Q2 to one end of DC motor.
- Connect base of transistor Q2 to collector of transistor Q1.
- Connect emitter of transistor Q2 to ground.
- Connect one end of capacitor C1 to collector of Q2 and the other end to pot through R2 resistor.
- Connect DC motor one end to collector of Q2 transistor and other end to positive power supply.
Note:
- For more advanced motor control features like direction control or overload protection consider using integrated circuits ICs designed for motor control applications.
- Take extra care while handing the electrical items.
Conclusion:
To conclude, while resistors offer a basic way to control motor speed they come at the cost of wasted energy and jerky operation.
A two transistor circuit provides a more efficient and refined solution.
By utilizing a potentiometer to control transistor behavior you achieve smooth and precise control over your DC motors speed.
This simple circuit packs a punch making it a great choice for basic motor speed control applications.
Leave a Reply