Transistors Based Megaphone Circuit uses transistor like amplifier.
Take weak sound from MIC and makes loud sound in speaker.
It is used in public talk, sports, rally anywhere we need loud voice.
The circuit have two TIP32 transistor in push-pull to boost sound.
It work with 12V battery or 12V DC power.
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Component | Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | ||
| 4.7k 1/4 watt | 1 | |
| Potentiometer 4.7k | 1 | |
| Capacitor | ||
| Ceramic 0.22µF | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | ||
| Transistors TIP32 | 2 | |
| Electret Microphone | 1 | |
| SPST Switch | 1 | |
| Speaker | 1 | |
| Battery | 1 |
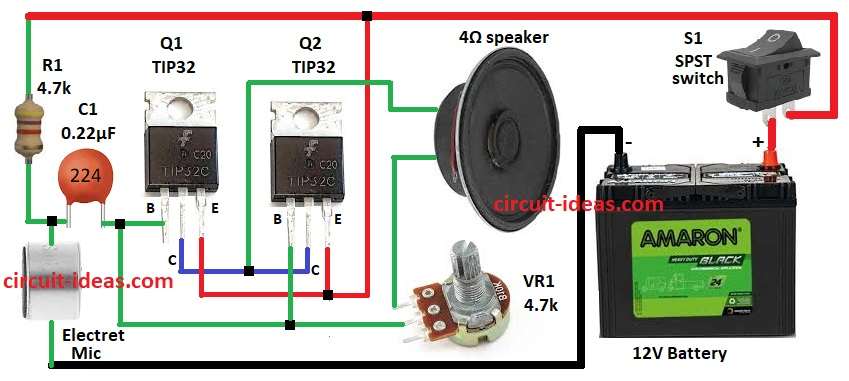
Electret mic is very important in this circuit as it change sound wave to small electric signal.
Q1 TIP32 work like preamp and make mic signal stronger.
Signal goes to Q2 TIP32 power amp and make sound more strong for speaker.
4Ω speaker change signal back to loud sound.
VR1 control volume and user adjust the loudness.
C1 block DC and pass mic frequency to transistor base.
R1 give bias to mic circuit.
S1 is power switch for whole circuit.
It uses 12V battery and is easy to carry and use.
Formulas with Calculations:
Below are the formulas with calculations for Simple Transistors Based Megaphone Circuit:
Voltage gain:
Av = β × (RL / RE)
where,
- β for TIP32 is 25 to100
- RL is for 4Ω speaker
- RE is for emitter resistor.
Power output:
P = V² / R
V = 10V and R = 4Ω
P = 100 / 4 = 25W.
Current from battery:
I = P / V
P = 25W and V = 12V
I = 25 / 12 = 2.08A.
How to Build:
To build a Transistors Based Megaphone Circuit following steps are needed to be followed to design our own circuit for connections:
- Gather parts from circuit diagram.
- Connect MIC to Q1 base through C1 and other MIC pin to GND.
- Connect R1 between C1, MIC and positive supply.
- Connect Q1 collector to Q2 collector.
- Connect Q1 emitter to Q2 emitter and positive supply.
- Q1 & Q2 base go to middle pin of VR1.
- VR1 second pin goes to 4Ω speaker and other speaker pin goes to collectors of Q1 & Q2.
- S1 switch goes between positive supply and 12V battery and battery negative go to GND.
Conclusion:
This Transistors Based Megaphone Circuit is easy and small megaphone for announcements.
Transistor TIP32 push-pull give clear sound.
It work on 12V battery portable and VR1 adjust volume and is simple to use.