This article teaches about 12V 5 Amp SMPS Power Supply Circuit with MOSFET and optocoupler.
It gives 12 volt power with 5 amp current and is used for small to medium electronic device.
This circuit works fast with not much heat and also save power.
What is a 12V 5 Amp SMPS Power Supply Circuit:
This 12V 5 Amp SMPS Power Supply Circuit gives stable 12V DC output and up to 5 amp current.
SMPS are used in many electronics where there is need of good power like LED lights, charging battery or other devices.
Next we will see how this circuit is build and some special formula makes it different.
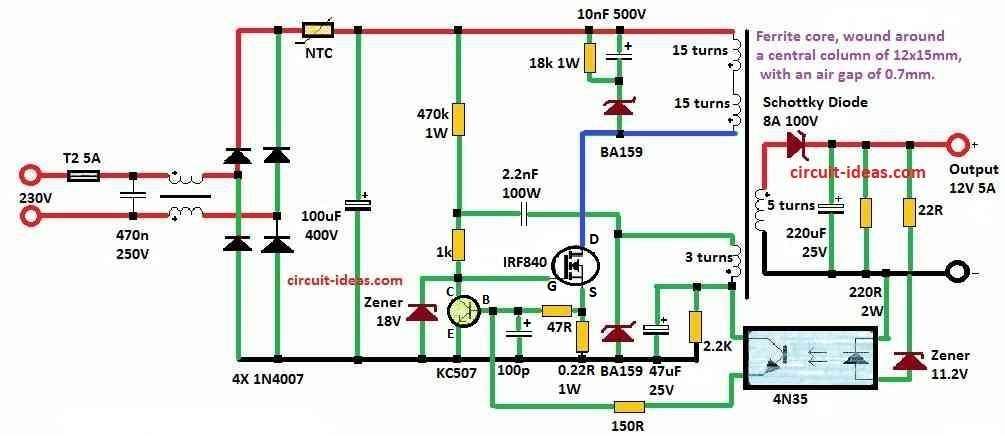
Circuit Working:
Parts List:
| Category | Component | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 470k 1/4W MFR | 1 |
| 1k 1/4W MFR | 1 | |
| 18k 1/4W MFR | 1 | |
| 47Ω 1/4W MFR | 1 | |
| 0.22Ω 1W MFR | 1 | |
| 150Ω 1/4W MFR | 1 | |
| 2.2k 1/4W MFR | 1 | |
| 22Ω 2W MFR | 1 | |
| 22Ω 1/4W MFR | 1 | |
| Capacitors | PPC 470nF 250V | 1 |
| Electrolytic 100μF400V | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 47μF 25V | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 220μF 25V | 1 | |
| PPC 10nF 500V | 1 | |
| PPC 100pF | 1 | |
| PPC 2.2nF 100V | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | Diode 1N4007 | 4 |
| Zener Diode 18V 1W | 1 | |
| Zener Diode 11.2V | 1 | |
| Schottky Diode BA159 | 2 | |
| Schottky Diode 8A 100V | 1 | |
| Transistor KC507 | 1 | |
| MOSFET IRF840 | 1 | |
| Optocoupler 4N35 | 1 | |
| NTC Thermistor | 1 | |
| Fuse 5 Amp | 1 | |
| Ferrite core EE | 1 |
Main job here is to control flyback inverter using MOSFET switch.
When setting up MOSFET gate get charge through 470k resistor and this make it turn ON.
MOSFET open fast and full because of positive feedback.
When 325V come to primary side then energy store in transformer core.
At same time voltage drop happen on 0R22 current sensing resistor when current goes up.
When drop reach 0.5V KC507 transistor turn ON.
Then KC507 pull down MOSFET gate voltage by making MOSFET turn OFF.
Feedback system help change transformer winding voltage fast by closing MOSFET quickly.
Electrolytic capacitor help move stored energy from transformer to output side smoothly.
Output voltage stay stable with help of Zener diode and optocoupler working together.
When output voltage goes low then Zener diode turns ON.
Current goes through 4N35 optocoupler LED and turn ON optocoupler transistor.
This increase voltage at KC507 base so it turns ON early when 0R22 drop is small.
The 0R22 resistor and KC507 limit max current for MOSFET is to 2.27A and this help protect from short circuit.
Transformer uses ferrite core with four 0.6mm wire for secondary winding and extra 0.4mm wires also.
Zener and optocoupler keep output voltage fluctuation to around 4%.
We can change Zener voltage and adjust number of turns on secondary coil to get different output voltage easily.
Formulas and Calculations:
Below is formula and calculation for simple 12V 5A SMPS circuit:
Maximum Current (Imax): = 2.27A
This means circuit can allow max 2.27 amp current safely.
If more current flow then circuit or part can break, heat too much or does not work.
Imax is used to be sure parts in circuit not get too much stress.
It is written in datasheet with other information like working temperature and lowest voltage.
Voltage Deviation (Vdeviation): = 4%
This 4% show how much voltage can go up or down from 12V target.
It is shown in percent mostly.
For example if output is 12V and Vdeviation is 4% then:
Minimum voltage: 12V – (4% of 12V) = 11.52V
Maximum voltage: 12V + (4% of 12V) = 12.48V
So voltage can be between 11.52V to 12.48V and still okay.
When building power supply Vdeviation help to keep output voltage in safe range.
Note:
These formulas help to set voltage and current limit of the circuit so it works safe and stable.
Safety Note:
This 12V 5 Amp SMPS Power Supply Circuit is not good for beginners as it is connected to high mains voltage which is very dangerous.
If design is not correct then mains voltage can come to output and give shock.
Even after removing plug the capacitors can still hold dangerous voltage.
Design the circuit at ones own risk.
As the writer does not take any responsibility if something break or someone get hurt.
Conclusion:
A 12V 5 Amp SMPS Circuit give easy and good way to power devices that need stable 12V DC up to 5A current.
Like normal power supply it uses high frequency switching to save energy and make less heat.
This design is useful for many things like small motor, LED lights and embedded systems.
Leave a Reply