This post shows how to make High Voltage Fence Charger Circuit.
It does not cost much and is safe to stop wild animals and keep our pets inside fence.
It cheap and easy to fix and is better than normal fence.
WARNING: Electric fence can kill if wrongly made.
Only do with adult help.
Circuit Working:
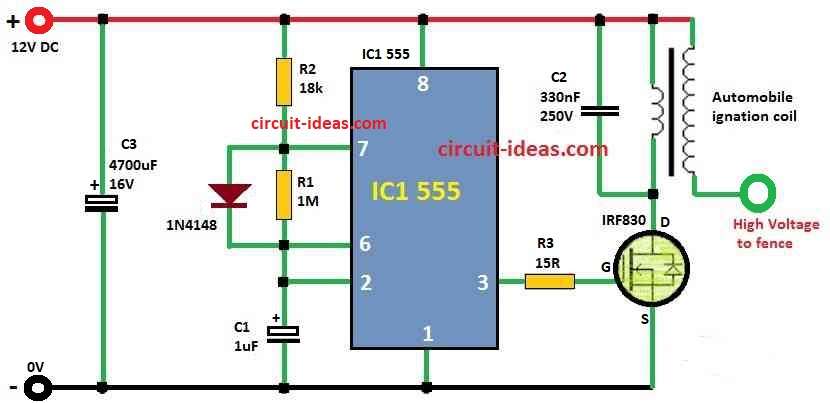
Parts List:
| Component | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified | |
| 18k | 1 | |
| 1M | 1 | |
| 15Ω | 1 | |
| Capacitors | ||
| PPC 330nF 250V | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 4700µF 16V, 1µF | 1 each | |
| Semiconductors | ||
| Diode 1N4148 | 1 | |
| MOSFET IRF830 | 1 | |
| IC 555 | 1 | |
| Automobile ignition coil | 1 |
Car ignition coil connect to power and through this circuit make high voltage pulse.
555 timer IC work in astable mode and make square wave many times.
Resistor R1 and capacitor C1 decide how fast pulse come.
If R1 is big then pulse become slow and C1 change speed and power of pulse.
555 timer send signal to MOSFET transistor gate.
Transistor like switch when is ON the high voltage pulse go from coil to fence wire.
R1, R2 and C1 help change pulse speed and power.
User can change parts to fit their fence.
Want stronger pulse? then use bigger transistor with more power.
How to Build:
To build a High Voltage Fence Charger Circuit follow these steps for connections:
- Connect wires a little bit high from ground before we use wire.
- Take wire off ground so no we do not touch by mistake.
- Use normal car ignition coil to make high voltage pulse.
- Use MOSFET transistor with 555 timer to control pulse well.
- Put resistor R1 to make pulse come about 1.3 times per second (1.3 Hz).
- Use resistor R2 to change how long transistor stays ON and make duty cycle near 2%.
- Capacitor C1 help control speed and power of pulse.
- If need more power or speed then use stronger transistor.
- If we make right this simple high voltage fence charger can give small shock with low current.
- It is not very dangerous for people or animals.
- Animals stay away after one painful shock.
- This circuit is good to add or replace normal fence and give more choice.
Conclusion:
For High Voltage Fence Charger Circuit always remember size and what we need from electric fence change and how we should build the charger circuit.
Also user must always stay safe when working with this kind of electric device.
Leave a Reply