18 Watt MOSFET Audio Amplifier Circuit is good for home sound, small PA or personal audio work.
It give medium power to sound signal.
This amplifier uses MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor).
It have many good things like to stay cool, less sound problem and work efficient.
MOSFET is 3-pin part which is used in many electric circuits.
It have special oxide layer that stop leak and make it work like JFET but is better.
MOSFET amplifier means amplifier use MOSFET.
It is good for linear amplifier because it handle less load.
Many circuits can use this type amplifier as it have many uses.
Circuit Working:
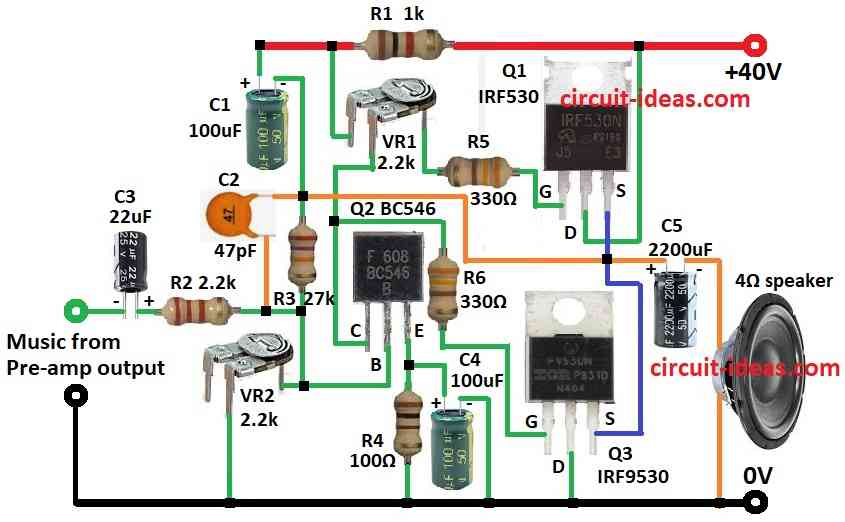
Parts List:
| Component | Value | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors (All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified) | ||
| 1k | 1 | |
| 2.2k | 1 | |
| 27k | 1 | |
| 100Ω | 1 | |
| 330Ω | 2 | |
| 2.2k | 2 | |
| Capacitors | ||
| Ceramic 47pF | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 100μF 50V | 2 | |
| Electrolytic 22μF 25V | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 2200μF 50V | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | ||
| MOSFET IRF530 | 1 | |
| MOSFET IRF9530 | 1 | |
| Transistor BC546 | 1 | |
| Speaker 4Ω | 1 |
This is small audio amplifier which makes strong sound using few parts and sound quality is good.
It uses shunt feedback with only one transistor, two MOSFETs, some resistors and capacitors which give 18 watts for 4 ohm speaker.
Need +40V power to work.
High voltage help push 4 ohm speaker with enough power.
Good power supply keep sound clean and give same power in different loads.
Best to use DC voltage regulator give 40V and more than 2 amps.
IRF530 N-channel MOSFET is used for sound boost and it is good because of low resistance and high input.
IRF9530 P-channel MOSFET work in push-pull with IRF530.
Together they give strong and stable output.
BC546 NPN transistor are used as driver and it help MOSFETs work better and give more gain.
If parts and design chosen well then this circuit give strong sound for many uses.
Formulas:
Some useful formulas help in making audio amplifier for power, parts value and how well it works.
Power Output Formula:
To find power output into load:
P = Vout² / Rload
where,
- P is the power in watts
- Vout is the RMS output voltage
- Rload is the load resistance like 4 ohm
To find how much voltage is increased:
AV = Vout / Vin
where,
- AV is the voltage gain
- Vout is the output voltage
- Vin is the input voltage
Power Supply Needs:
Power supply must give enough voltage and current.
Current from supply is:
Isupply = Poutput / Vsupply
where,
- Isupply is the supply current
- Poutput is the power output
- Vsupply is the supply voltage
To stop MOSFETs from getting hot and find how much power they waste:
Pdissipated = VDS × ID
where,
- Pdissipated is the power wasted
- VDS is the drain to source voltage
- ID is the drain current
Use heatsink if this value is high.
Capacitor Value for C3 and C5:
Used for coupling and for bypassing.
Formula to find capacitor:
C = 1 / (2πfcR)
where,
- C is the capacitor value
- fc is the cutoff frequency
- R is the resistance it connects to
Feedback Network:
Amplifier gain also set by feedback resistors:
ACL = 1 + Rf / Ri
where,
- ACL is the closed loop gain
- Rf is the feedback resistor R3
- Ri is the input resistor R2
These formulas help build and understand audio amplifiers and check how they perform.
How to Build:
To build a 18 Watt MOSFET Amplifier Circuit follow the below mentioned steps:
- Gather all the parts as shown in circuit diagram
- Q2 collector goes to gate of Q3 through R6 and to one leg of preset VR1.
- Q2 base connects to first leg of VR2 and second leg of VR2 goes to ground.
- From base of Q2 connect R3 and C1 to +40V.
- Q2 emitter goes to ground through R4 and C4 also connects to ground between emitter and R4.
- Between base of Q2 and R3 connect R2 and C3 in series and this goes to music input from preamp.
- Q1 gate connects from R5 to middle leg of VR1.
- Q1 drain goes to +40V, and source of Q1 connects to source of Q3.
- Q3 gate connects to Q2 collector and Q3 drain goes to ground, Q3 source connects to Q1 source.
- C2 connects between R2 and R3 and one side of speaker goes through C5 to this point and other side of speaker goes to ground.
- R1 connects to +40V supply.
Safety Tips:
- Handle and test carefully.
- Use proper heat sinks for MOSFETs.
- Double check power connections before turning ON.
- Use quality parts and strong DC power supply.
Conclusion:
This simple 18 Watt MOSFET Audio Amplifier Circuit gives strong sound using few parts.
With good power supply and safety steps it work well for many audio uses.
It is cheap and good for home projects.
References:
Does a MOSFET amplifier sound different than a standard transistor amp?