A Frequency Divider Circuit take signal with high frequency and give signal with lower frequency.
It changes the signal in way to reduce frequency.
Two common ICs used for this:
IC 4017 Decade Counter:
- It has 10 outputs (Q0 to Q9).
- One output goes high for each clock pulse.
- It can work in many ways.
- Here we used it in astable mode to make square wave and this square wave work as clock for 4017 counter.
Circuit Working:
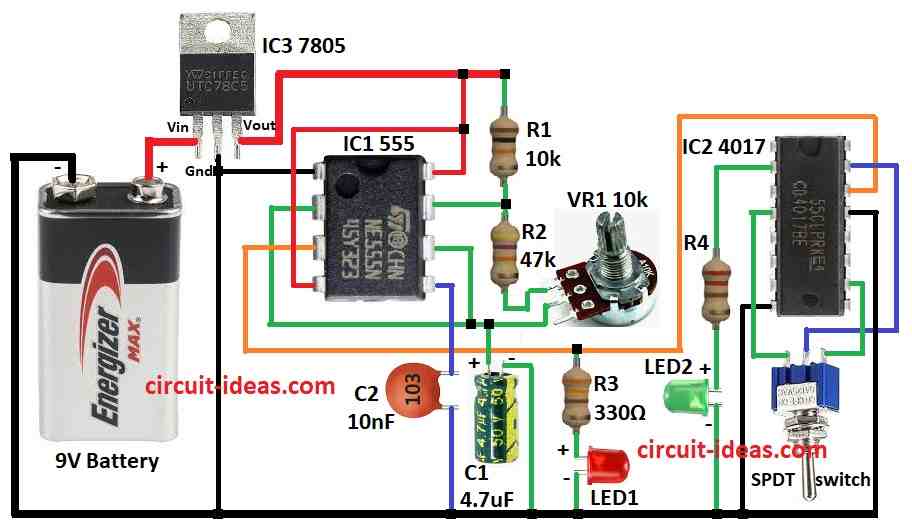
Parts List:
| Category | Item | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors (All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified) | 10k | 1 |
| 47k | 1 | |
| 330Ω | 1 | |
| R4 220Ω | 1 | |
| Potentiometer 50k | 1 | |
| Capacitors | Ceramic 10nF | 1 |
| Electrolytic 4.7μF 25V | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | IC 555 | 1 |
| IC 4017 | 1 | |
| IC 7805 | 1 | |
| LED red 5mm 20mA | 1 | |
| LED green 5mm 20mA | 1 | |
| SPDT switch | 1 | |
| 9V Battery | 1 |
We can make simple frequency divider using two ICs and here it is how it work:
Set Input Frequency:
IC 555 is used as astable multivibrator and it make square wave signal again and again.
We can change this frequency using one potentiometer like volume knob.
One LED1 is connected to show this frequency by blinking.
Split the Frequency:
IC 555 output goes to IC 4017 counter and this chip count clock pulses.
We use switch to connect reset pin which is pin 15 to different output pins like Q pins to change how it divides.
Divide by 2 (f/2):
Reset pin connect to Q2.
During first pulse Q1 become high and LED2 blinks.
During second pulse Q2 become high and counter reset to Q0.
So LED blink every 2 pulses with half frequency.
Divide by 4 (f/4):
Reset pin connect to Q4.
Counter goes to Q0, Q1, Q2 and Q3.
On Q4 it reset backs to Q0.
Now LED blink once every 4 pulses with 1/4 frequency.
Main Idea:
Counter skip some pulses and that make output frequency lower.
Power Supply:
IC 7805 give stable voltage, and one 9V battery power the whole circuit.
Formulas:
Here are main formula and things to know for making astable multivibrator using IC 555 for frequency divider:
Output Frequency (fout):
Frequency depends on resistor R1, R2 and capacitor C1.
Formula:
fout = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 × R2) × C1)
where,
- R1 and R2 are resistors connected to IC 555
- C1 is timing capacitor
Duty cycle means how long output stays high in one full cycle.
Formula:
Duty Cycle = (R1 + R2) / (R1 + 2 × R2)
Note:
Change R1, R2 and C1 values to get needed output frequency and duty cycle.
We can use IC 555 like this to build astable multivibrator for frequency divider circuit.
How to Build:
To build a Frequency Divider Circuit follow the below mentioned steps for connections:
- Pin 1 of IC1 555 connects to ground.
- Pin 2 connects to pin 6 using capacitor C1.
- Pin 3 of IC1 connects to pin 15 of IC2 4017.
- Pins 4 and 8 of IC1 connects to +9V battery.
- Pin 5 connects to ground using capacitor C2.
- Resistor R2 connects between pin 7 and top leg of VR1 pot.
- Resistor R1 connects between pin 7 and +9V.
- Resistor R3 + LED1 connect in series from pin 3 to ground.
VR1 potentiometer and SPDT switch connection:
- One leg connects to R2
- Other leg connects to pin 2 and pin 6
- Resistor R4 + LED2 connects in series from pin 2 of IC2 to ground.
- Pin 4 of IC2 connects to 3rd leg of SPDT switch.
- Pins 8 and 13 of IC2 connects to ground.
- Pin 10 connects to 1st leg of SPDT switch.
- Pin 14 connects to pin 3 of IC1.
- Pin 15 connects to center leg of SPDT switch.
Power using IC3 7805:
- Vin connects to +9V battery
- GND connects to negative supply.
- Vout connects to + pin of IC1 circuit which is regulated to 5V supply
Safety Tips:
- Check wires and parts connected tight and right.
- Do not leave live circuit alone especially when connected to other devices.
- If unsure ask someone skilled or use trusted guides online.
- Careful wiring helps avoid damage or shock.
Conclusion:
This easy Frequency Divider Circuit uses IC 555 to make signal with adjustable frequency.
IC 4017 counts signal and skip pulses to divide frequency.
By linking reset pin to different output Q pin, we can divide frequency by 2, 3, 4, etc.
It is a very easy way to learn how frequency divider works using common ICs.
Leave a Reply