Have fun making this Simple Lie Detector Circuit using Transistors.
Real lie detectors are very hard and complicated so this one is not perfect.
But it is fun way to see how body react when stress.
This circuit works by checking sweat changes to know if someone tell truth or lie.
When people are scared or nervous they sweat more.
Be careful: Do not use this for real lie test use it just for fun only.
What is a Lie Detector Circuit:
Lie detector circuit is also called polygraph or truth checker is electric device.
It checks body signs that my show lying.
Idea is simple when person lie or feel stress body changes little without knowing.
Lie detector watch these feelings and try to know if person says truth or lie.
How to make it and how circuit work is shown below:
Circuit Working:
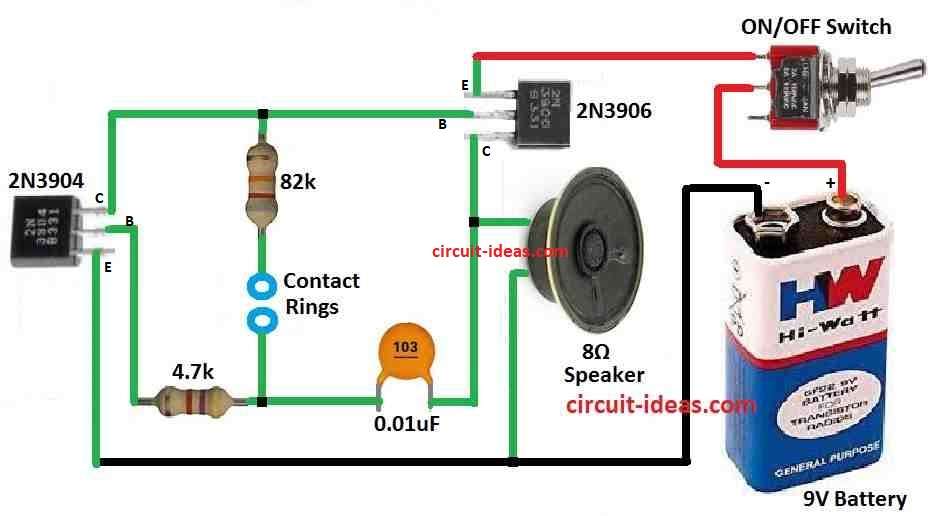
Parts List:
| Category | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 4.7k CFR, 82k CFR | 1 each |
| Capacitor | Ceramic 0.01µF | 1 |
| Semiconductors | Transistors 2N3904, 2N3906 | 1 each |
| Speaker 8Ω | 1 | |
| ON/OFF Switch | 1 | |
| Battery 9V | 1 | |
| Blue Rings | 2 |
This circuit starts working when person put fingers on blue rings and switches ON the power.
If fingers is dry and person is calm then speaker make low sound that mean there is no stress.
But when person feel scared or nervous then small amount of salty water come from fingers.
Circuit catches this fast and speakers sound become more sharp and loud.
Sound changes show person maybe having stress and maybe telling lie or not telling full truth.
Because of this smart way lie detector circuit help see feelings and maybe find hidden truth.
Formula:
Below is formula for finding resonant frequency of LC circuit:
f = 1 / 2π√LC
where:
- f is the resonant frequency in hertz Hz.
- L is inductance in henry H.
- C is capacitance in farads F.
- π (pi) is math number about 3.14159.
- √ means square root.
This formula say frequency goes lower when L or C become bigger.
So more inductance or capacitance = lower frequency.
Opposite is also true like small L or C = higher frequency.
Note:
This formula only works good when circuit have no resistance.
Actual circuits always have some resistance so real frequency may change a little and become weaker.
Many electronics use this idea like oscillators, filters and radio tuning.
How to Build:
To build a Simple Lie Detector Circuit follow the below mentioned connections steps:
Get the Transistors Ready:
- First put PNP transistor 2N3906 and NPN transistor 2N3904 in right place.
- Be sure wires and parts are connected good for smooth working of circuit.
Connect the Blue Rings:
- Put the blue rings at correct place in circuit.
- These rings are for touching with fingers and they help to find small body changes.
Connect to Power Supply:
- To give power to circuit add one 9V battery.
- Check all wires are connected properly and power must be stable for best result.
Build the Feedback Oscillator:
- This lie detector uses 2 transistor feedback oscillator as main part.
- Use the above formulas to find correct resistor and capacitor values for good frequency.
- This help the oscillator work and find small changes in body signals.
Connect the Audio Output:
- Add 8 ohm speaker to circuit for sound output.
- Speaker makes different sounds based on circuits frequency.
- This will help to understand if person maybe lying or not.
Conclusion:
Simple Lie Detector Circuit using Transistors are used in police work, jobs and more.
But many people still do not agree if they always work correct.
Success of lie test depend on many things like how person feel or how well they hide emotion.
Also lie detectors have to follow law rules.
In many countries lie test result can be used as proof in court.