Mains AC Power Supply Failure Buzzer(Alarm) Circuit is small device.
It makes sound (buzzer) when AC power goes OFF.
It helps us to know power gone and is useful if we have important machine to know power goes at night.
It uses one switch called relay.
When power is there the relay works and stops buzzer sound.
When power is cut then relay stops contacts change and buzzer makes sound.
Circuit Working:
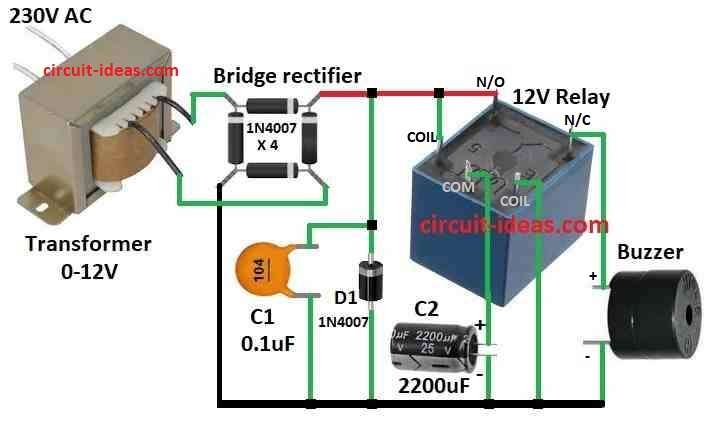
Parts List:
| Component Type | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitors | Ceramic 0.1μF | 1 |
| Electrolytic 2200μF 25V | 1 | |
| Semiconductors | Diode 1N4007 | 1 |
| Bridge Rectifier 1N4007 | 4 | |
| 12V Relay | 1 | |
| Buzzer | 1 | |
| 12-0-12V Transformer | 1 |
After making circuit same like diagram plug in to turn ON.
Then turn OFF the power and wait the buzzer will beep and this way we test the circuit.
This work like an emergency light, buzzer sounds when power goes.
Circuit is simple.
Transformer change high 220V AC to low 12V AC when power is ON.
Bridge rectifier then changes 12V AC to DC.
Bridge rectifier has 4 special diodes and it makes current go one way in each half of AC.
Output is DC but direction is the same.
Good thing is no need of a special transformer.
After DC is made current goes through capacitor C2.
C2 clean bad noise from current and it is also called smoothing capacitor.
Another capacitor C1 start charging and then relay turns ON.
When power goes OFF the relay goes back and the circuit connects buzzer to capacitor.
Buzzer uses power from capacitor and beep until capacitor is empty.
If capacitor is bigger then buzzer beeps longer.
In this setup the buzzer uses 0.310 Amps.
If using DC power supply then no need of transformer and rectifier.
Formulas:
Transformer Turns Ratio:
This formula help find output voltage of transformer using coil turns and input voltage:
Vo / Vi = Ns / Np
where:
- Vo is the output voltage for 12V AC
- Vi is the input voltage for 220V AC
- Ns turns in secondary coil
- Np turns in primary coil
Use this if we want to know how transformer changes the voltage or if we use different transformer.
Capacitor Charging Time:
We can find how long capacitor C1 takes to charge when power is ON, then we use this formula:
t = CV / I
where:
- t is the time in seconds
- C is the capacitance of C1 in farads
- V is the voltage for 12V DC
- I is the charging current which depends on circuit resistance
Use this if we want to know how long capacitor takes to full charge.
How to Build:
To build a Mains AC Power Supply Failure Buzzer Circuit follow the below mentioned steps for circuit connections:
- Put all parts same like shown in diagram.
- Connect relay common pin to ground using capacitor C2.
- Connect relay coil between positive and negative power lines.
- Connect buzzer to NC (normally closed) pin of relay and to ground.
- Connect capacitor C1 from positive line to ground.
- Connect diode D1 between positive line and ground.
- Connect positive pin of bridge rectifier to positive line of circuit.
- Connect negative pin of bridge rectifier to negative line.
- Connect 12V AC wires from transformer to AC input pins of bridge rectifier.
Safety Tips:
- Work only if we know how to handle electricity safely.
- Mains AC is dangerous and it can kill or hurt badly.
- Always turn OFF and disconnect power before touching the circuit.
- Use parts with correct voltage ratings.
- If not sure then buy ready made power fail buzzer from electronics shop.
Conclusion:
Mains AC Power Supply Failure Buzzer(Alarm) Circuit is useful to tell when power is gone.
It turns ON when main power is cut like in emergency light.
Circuit is simple where relay controls the buzzer, transformer reduces the voltage, bridge rectifier changes AC to DC and capacitors stores and filters power.
References:
What is T1 in this circuit for ‘Mains power failure alarm’? [closed]
Leave a Reply