This post show how to make a Alternate Red Green LED Flasher Circuit using red and green LED.
It is fun and easy circuit, that is a reason so many people like this project.
This circuit uses two BC547 transistor and they help red and green LED blink one by one.
What is a Alternate Red Green LED Flasher Circuit:
Red green LED flasher circuit is small easy circuit which makes red and green LED blink one after other.
People use this type of circuits for decoration like for signal or festival light when red and green flash are needed.
Circuit Working:
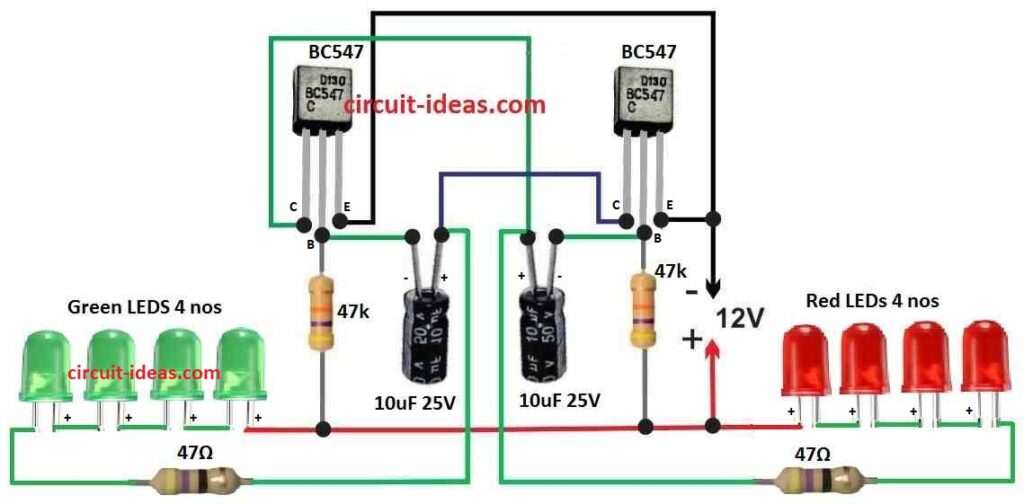
Parts List:
| Type | Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors | 47k | 2 |
| 47Ω | 2 | |
| Capacitors | Electrolytic 10µF 25V | 2 |
| Semiconductors | Transistor BC547 | 2 |
| LEDs Red and Green 20mA 5mm | 4 each |
This circuit uses BC547 transistor like astable multivibrator which makes square wave signal.
This signal connects to LEDs and make them blink one after one.
10uF capacitor and 47k ohm resistor control how fast LEDs flash.
If we change these parts flash speed also changes.
47 ohm resistor is in line with LEDs which stops too much current and keep LEDs safe.
Red and green LEDs are connected in series so they all get same current.
LED anodes connects to positive wire and cathodes connects to transistor collector.
Power:
Circuit need 12V DC power to work.
Be sure positive and negative wire connect correct or else parts may get damage.
Testing:
When power is ON red and green LEDs start blinking alternately.
We can try different resistor or capacitor to make blinking faster or slower.
Formula:
Below is basic formula for astable multivibrator frequency:
Frequency (f):
f = 1 / (1.4 × (R1 + R2) × C)
where:
- f is frequency to how fast it blink
- R1 and R2 are resistors which are both 47k ohm
- C is capacitor with 10uF value
How to Build:
To build a Alternate Red Green LED Flasher Circuit follow the below mentioned steps:
Transistor Connection:
- Connect emitter of both BC547 transistors to ground of negative side.
- Collector of both transistor connects to positive line with 47 ohm resistor in between.
- Base of each transistor connects to middle point of one 10uF capacitor and one 47k resistor.
LED Connection:
- Put 4 green 5mm LEDs in series with one 47 ohm resistor and connect this to collector of first BC547.
- Do the same for 4 red 5mm LEDs in series with 47 ohm resistor and connect to collector of second BC547.
- Anodes long leg of both red and green LED strings connects to positive line.
Uses and Application:
- We can use red-green LED flasher for decoration like for festivals, events or home lights.
- Blinking red and green light look nice and attract people.
- Also can use this circuit for signal purpose like alarm system or status display.
- Red and green light can show different state or condition.
Conclusion:
For people who like electronics making Alternate Red Green LED Flasher Circuit is fun job.
This easy circuit work good for many things like signal or decoration, because it make nice blinking lights.
If we want to change how fast it blink or make it look more cool then we can try using different parts like other resistor or capacitor.