Simple Contact MIC Circuit is special mic, it can record weird sound when we put it in different things.
If we give it small electric power it can even make sound by itself.
We can use contact mic and simple wire setup to make normal guitar sound like electric guitar if we want it louder.
Inside mic there is thing called piezo disc which makes power when we press it.
This help mic to catch small shake like knock or tap.
Also small speaker that make beep sound can use this too.
Circuit Working:
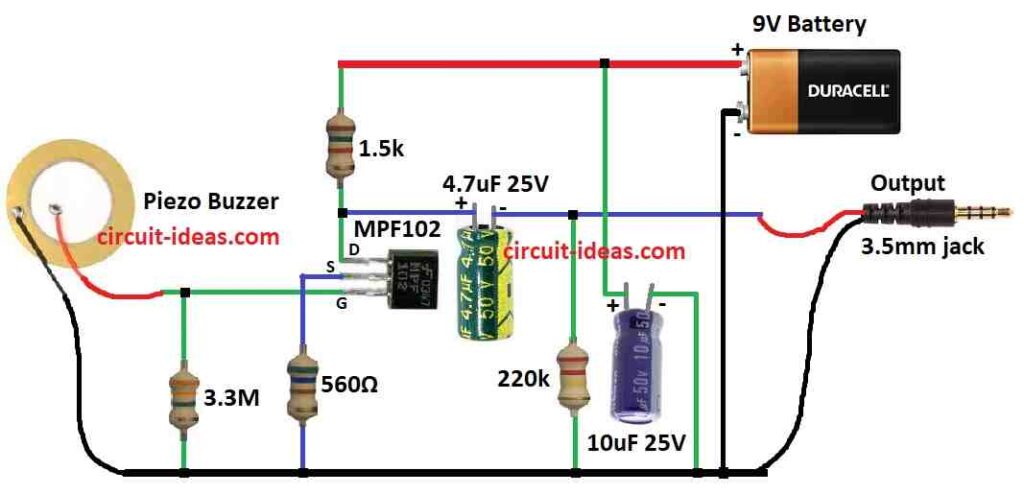
Parts List:
| Component | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Resistors | |
| 3.3M 1/4 watt | 1 |
| 1.5k 1/4 watt | 1 |
| 560Ω 1/4 watt | 1 |
| 220k 1/4 watt | 1 |
| Capacitors | |
| Electrolytic 4.7µF 25V | 1 |
| Electrolytic 10µF 25V | 1 |
| Semiconductors | |
| JFET MPF102 | 1 |
| Piezo Buzzer | 1 |
| Battery 9V | 1 |
| Jack 3.5mm | 1 |
Main part is preamp it is simple circuit and it matches piezo signal.
Piezo and preamp together make acoustic guitar sound electric.
How circuit work:
The JFET part called MPF102 is main thing here.
Its source pin connects to 9V battery.
1.5k resistor send power to source.
Drain pin is used for both input and output signal, that is why we call this a common drain circuit.
Source goes to battery ground with 220k resistor is on drain side.
MPF102 is used in this circuit an if we use MPF120 it also works the same.
When there is no signal bias voltage make small current flow.
It put source voltage between battery and ground and is not too high and not too low.
This is good for small audio signals which helps avoid sound distortion.
Input signal goes to gate of JFET.
It passes through big resistor like 3.3M and this resistor lets AC signal go in.
How JFET works:
JFET take signal and make it big with its amplifier.
A 560Ω resistor control voltage drop and this is between source and gate.
Bias voltage keep JFET working in middle which is not too open and not too closed.
When signal come it changes the gate voltage.
This make more or less current go through JFET.
Current changes becomes voltage change because of 1.5k resistor at source.
So small signal at gate control big current and that is how it get amplified.
Output signal show up between source and ground.
AC signal goes through circuit but DC is blocked by 4.7uF capacitor.
Signal goes out through this capacitor even when source is more positive than ground.
Only AC can pass and DC stays blocked.
Formula:
This formula show voltage gain (Av) of special type amplifier.
It is called common source (CS) amplifier and it uses FET transistor.
Formula is:
Av = gm * Rs / (1 + gm * Rs)
Now what these mean:
Av is voltage gain which tells how much louder output is than input.
If Av is more than 1 then amplifier make signal bigger.
gm is transconductance and it tell how much output current change when input voltage change.
Rs is source resistor and it is connected to source pin of FET.
How formula work:
If gm is big then voltage gain also become big.
input voltage change make big output current.
If Rs is big then gain become small because some input voltage drop across Rs which is less voltage left for FET to use.
Think of (1 + gm * Rs) like voltage divider, it takes some voltage away from input.
If Rs is very small and gm is big then (1 + gm * Rs) is close to 1 and so gain is high.
But if Rs become big and closes to gm then (1 + gm * Rs) become big too and gain goes down.
Important to remember:
This formula is only for common source type FET amplifier.
Other amplifier types have different formulas.
This formula show possible voltage gain based on FET and Rs value.
In actual life other things like FET behavior and output limits can change the real gain.
How to Build:
Building a Simple Contact MIC Circuit follow the below mentioned connection steps:
Put Parts on PCB:
- First put MPF102 JFET transistor on PCB board.
- Take 220K resistor and connect one side to JFETs drain and other side will connect to battery +9V.
- Connect JFETs source to battery ground.
- Now take 1.5k resistor and connect it to JFETs source pin.
- Connect guitar cable to JFETs gate pin through 3.3M resistor.
Add Piezo Transducer:
- Now put piezo disk in circuit.
- Connect one side of piezo to source and other side goes to ground.
Add Capacitor:
- Take 4.7uF capacitor and connect between source and ground.
- Only AC signal can go through this capacitor as it blocks DC voltage.
Check All Wires:
- Look at all connections again and be sure wires are not loose.
- Check circuit and match with circuit diagram.
Power the Circuit:
- Connect battery, +9V goes to right place and ground goes to correct pin.
Test the Circuit:
- Plug guitar cable into amplifier with other side of cable goes to circuit output.
- Now tap or press piezo and listen to amp.
- Change volume or gain if needed.
Adjust and Tune:
- Try different resistor values if sound is not good.
- Change parts to get better sound for your instrument.
- Every setup may need different settings.
Put in Box (Optional):
Conclusion:
While building Simple Contact MIC Circuit be careful with electronics.
Understand the circuit fully before anyone builds it.
If anyone do not feel safe or do not know much about circuits ask for help or learn more first.
References:
What is a good circuit for recording a piezo contact microphone or an electric guitar pickup?
Piezoelectric contact mic for Audio line in Teensy 4.0 Rev D Board High Voltage issue
Leave a Reply