In this AC Power Outlet with Timer Circuit think about a normal plug goes in wall but this one have a timer built-in like small control panel.
This is called a timer plug or outlet timer.
We can plug other device into it.
Inside, small chip work like a brain and it is called 555 timer.
This chip send electric in square wave like a fast ON/OFF switch.
Speed of wave change by small parts with resistors and capacitor which look like tiny knobs and battery.
This speed decide how fast our device turn ON and OFF.
We can use online calculator to know how long device stays ON and OFF.
So this small timer help us set lamp to turn ON at sunset and OFF at sleep.
Or make Christmas lights blink on time!
Circuit Working:
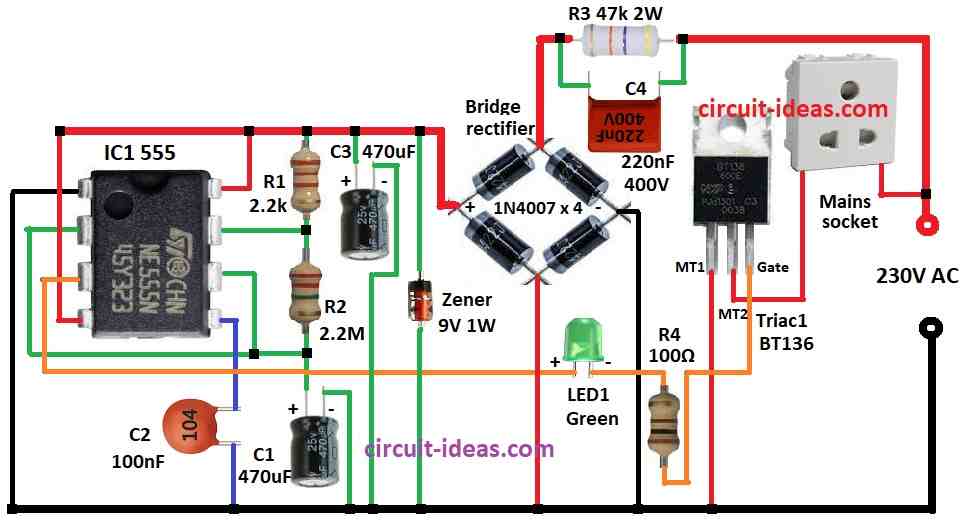
Parts List:
| Component Type | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Resistors (All resistors are 1/4 watt unless specified) | ||
| 2.2k | 1 | |
| 2.2M | 1 | |
| 47k 2W | 1 | |
| 100Ω | 1 | |
| Capacitors | ||
| Ceramic 100nF | 1 | |
| PPC 220nF 400V | 1 | |
| Electrolytic 470μF 25V | 2 | |
| Semiconductors | ||
| IC 555 | 1 | |
| Triac BT136 | 1 | |
| LED green 5mm 20mA | 1 | |
| Zener diode 9V 1W | 1 | |
| Bridge rectifier diodes 1N4007 | 4 | |
| Mains socket | 1 |
This circuit uses AC power from wall directly.
No need for step-down transformer.
How it work:
AC Lowering:
Resistor R3 and capacitor C4 together reduce AC voltage.
C4 block sudden voltage changes with capacitive reactance.
R3 help C4 discharge when power goes OFF.
AC to DC Conversion:
Bridge rectifier change low AC to pulsing DC.
Voltage Control:
Zener diode keep DC voltage steady at about 9V.
Capacitor C3 remove small ripples before power goes to timer.
Timer Control:
555 timer work in astable mode which is always ON.
It make square wave pulses with ON/OFF signals.
It changes resistor R2 or capacitor C1 to change ON/OFF time.
Power Switching:
TRIAC BT136 act like switch between neutral and outlet.
Gate of TRIAC connect to timer output.
When timer send high pulse then TRIAC turns ON and power goes to outlet.
When timer send low pulse then TRIAC turns OFF and outlet stops the power.
Result:
Device plug in timer plug will turn ON/OFF again and again.
With current parts it stays ON 23 mins and gets OFF 23 mins.
If we only want auto shut-off one time then make timer monostable.
Formula:
To control AC power we can make astable multivibrator circuit using:
Resistors, Capacitors, Transistors, IC (timer chip) and TRIAC (for AC switching)
This circuit turn AC load ON and OFF again and again.
Simple Circuit Idea:
In diagram:
R1 and R2 are the resistors
C1 and C2 are the capacitors
Time Formula:
Time for ON and OFF (T) is:
T = 0.693 × (R1 + R2) × C1
This formula tell how fast circuit switch controls ON/OFF time of AC device.
We can change part values with resistors and capacitors to match our needs.
Sometimes extra parts are needed for special uses.
How to Build:
To build a AC Power Outlet with Timer Circuit follow the below mentioned steps for connections:-
- Pin 1 of 555 connects to ground
- Pin 2 connect to pin 6
- Pin 3 connect to TRIAC gate through R4 and LED1
- Pin 4 connects to positive supply
- Pin 5 connects to ground through C2
- R2 connects between pin 7 and pin 6 and 2
- R1 connects between pin 7 and positive supply
- C1 from pin 6 and 2 connects to ground
- Pin 8 connects to positive supply
- C3 connects from positive supply to ground
- Zener Diode of 9V connects between positive and ground
- C4 and R3 are in series with AC line to drop voltage
- Bridge Rectifier 4 × 1N4007 convert low AC to DC
TRIAC1:
- MT1 connects ground
- MT2 connects one side of AC socket
- Other side of socket connects to 230V AC
- Gate of pin 3 of 555 connects through R4 and LED1
Safety First:
- AC is dangerous we should be careful.
- If not sure about electronics then ask licensed electrician to help.
- Use parts rated for 230V AC, with wrong parts may burn or catch fire.
- Always unplug before touching the circuit and also do double check.
- Ground the box properly to avoid shock.
- Do not build this if anyone do not fully understand high voltage risk.
Conclusion:
With this AC Power Outlet with Timer Circuit we can control AC appliance with timer.
It is smart and useful but safety is most important.
If AC makes us nervous then use safer method or ask professional for help.
Leave a Reply